AWS dominates the cloud computing industry, and rightfully so. With its simplified server and service setup, and powerful monitoring solution, AWS is the go-to choice for over 1.45 million organizations worldwide. Despite all that, AWS monitoring can still be a daunting task.
Therefore, it is crucial to understand AWS monitoring best practices completely to ensure that your cloud-based tasks run efficiently. Today, we’ll discuss 10 AWS monitoring best practices you must know 2026. But let’s sort the basics first.
What is AWS Monitoring?
AWS monitoring is the practice of checking on the health and performance of your Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud infrastructure. The goal is to identify issues before they escalate, cause significant disruption, and ensure that your AWS resources run efficiently.
You can track metrics like CPU usage, memory usage, network traffic, and storage capacity. You can also set up alerts to notify you of any anomalies in your infrastructure. This way, you can take timely action to prevent any potential downtime or performance issues.
Why is monitoring AWS important?
Monitoring AWS is crucial for several reasons. When you’re monitoring AWS, you’re constantly on the lookout for any signs of trouble, from sneaky resource hogs to suspicious security breaches.
Let’s look at these reasons in detail:
- Identify and resolve issues: Monitoring AWS helps you detect and resolve issues before they escalate and degrade operational efficiency.
- Ensure high availability: AWS monitoring helps keep your resources available and enables timely action to prevent downtime.
- Optimize resource utilization: AWS monitoring can identify opportunities to reduce costs. This enables you to optimize your resource utilization.
- Ensure security: AWS monitoring helps protect your cloud infrastructure by detecting suspicious activity and security breaches. You can also follow multiple AWS monitoring and alerting best practices for the same.
- Compliance and governance: Monitoring AWS helps ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards, including HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR. It also enables you to enforce governance policies and maintain audit trails.
10 AWS Monitoring Best Practices You must know in 2026
Software engineers usually rely on application instrumentation frameworks to get insights into application issues. These frameworks provide valuable insights into the performance of code and applications and can include tools like breakpoints/debuggers and logging instrumentation.
However, relying solely on manual processes is not always practical in larger, multi-cloud environments. To help ensure AWS observability in these more complex environments, you must keep the following AWS monitoring best practices in mind.
1. Define Monitoring Goals
According to a survey, 87% of IT decision-makers reported that monitoring and observability were their organizations’ top priorities. But to do that effectively, you need to first define your monitoring goals.
Focus on the following questions:
- What are you trying to achieve?
- What are your top priorities?
Once you have the answers, you can develop a monitoring strategy that outlines the metrics you’ll use to track your systems’ health.
What next? Have clear processes in place for responding to alerts and incidents. In the event of an incident, you’ll need to quickly identify the root cause and take action before it escalates.
Create an incident response plan with well-defined steps you’ll take to minimize the impact of any issues. You’ll take steps to minimize the impact of any issues.
👉Stop juggling multiple AWS tools and dashboards. Try Middleware for AWS monitoring
2. Collect and Analyze Data from all Areas of your AWS Environment
Multiple Amazon services (and platforms) have different roles and specifications. Some might seem like a better fit for your needs, and some won’t. However, creating a monitoring plan that collects data from all areas of your AWS environment is essential.
With complete visibility, you can efficiently collect and analyze data, enabling you to quickly address multi-point failures as they occur.
It’s important to have answers to basic monitoring questions to save time when navigating different areas of your cloud infrastructure. Some of these questions include:
- What resources are being monitored?
- Who is responsible for monitoring them?
- How often are they monitored?
We at Middleware integrate with CloudWatch and CloudTrail, enabling you to collect data from all areas of your AWS environment.
3. Use the Right AWS Monitoring Tools
The right AWS monitoring tool is essential for effectively monitoring your AWS infrastructure. There are many monitoring tools available, so selecting the right one can be challenging.
Choose a tool that fits your needs and clearly understands your AWS infrastructure’s performance. Consider the following factors while selecting the right AWS monitoring tool for your organization:
- Level of automation to reduce routine tasks
- Ease of use and customization capabilities
- Cost-effectiveness and its value for money
- The tool’s ability to integrate with your existing infrastructure
- How well it can monitor your infrastructure various components, such as servers, applications, and databases.
Consider Middleware’s full-stack cloud observability platform, which offers real-time visibility into your AWS monitoring infrastructure. You can use its comprehensive tools, automated alerting, anomaly detection, and customer dashboard to monitor your AWS environment.
It supports monitoring of various AWS services, including EC2, RDS, Lambda, and more. Our platform also integrates with other AWS tools and services, such as CloudWatch, CloudTrail, and X-Ray.
Other alternatives include Datadog, Dynatrace, and AppDynamics.
4. Automate Monitoring Tasks as much as possible
Automating monitoring tasks is essential to maintaining a stable and efficient AWS infrastructure. It lets you can free up valuable time for your team to focus on more strategic tasks and minimize the risk of human error.
Here are some tips to help you automate your monitoring tasks in AWS:
- Use AWS CloudFormation: It lets you define your infrastructure as code and automate the provisioning and configuration of your resources.
- Use AWS Lambda: A serverless computing service that lets you run code in response to events or triggers. You can automate monitoring tasks like log processing and data aggregation using AWS Lambda.
- Use AWS Config: This service allows you to track changes to your AWS resources and enforce compliance policies. You can use Config rules to automate monitoring tasks, such as checking for security vulnerabilities and resource misconfigurations.
- Leverage machine learning: Machine learning algorithms can help you detect patterns and anomalies in your data that may be difficult to identify manually. AWS offers a range of machine learning services, such as Amazon SageMaker and Amazon Rekognition, for monitoring and analysis.
5. Setup Alerts
Setting up alerts is a crucial aspect of AWS monitoring. It enables you to receive notifications during incidents. This allows you to take quick action and resolve issues before they affect your end users.
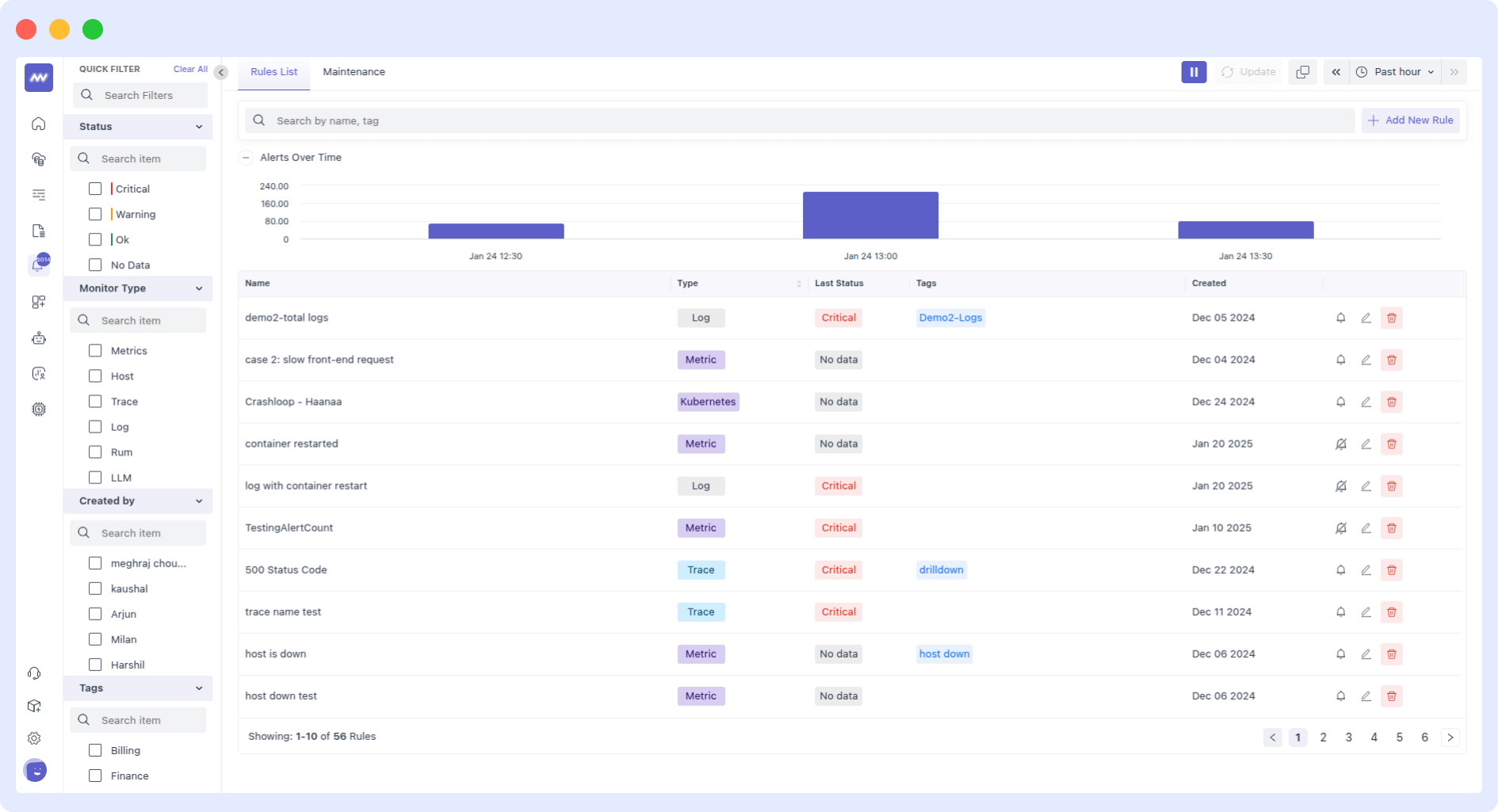
Ensure that these alerts are routed to the right person or team. Here are some best practices for setting up alerts in AWS:
- Define appropriate thresholds for your alerts. They should be based on your infrastructure’s specific requirements. Setting thresholds too high or too low can lead to unnecessary alerts or missed critical issues.
- Configure notification preferences for alerts, including notification method (email, SMS, etc.), recipient, and severity level. Use AWS Simple Notification Service (SNS) to route notifications to multiple recipients or endpoints.
- Use escalation policies to route alerts to the appropriate person or team based on severity or time sensitivity.
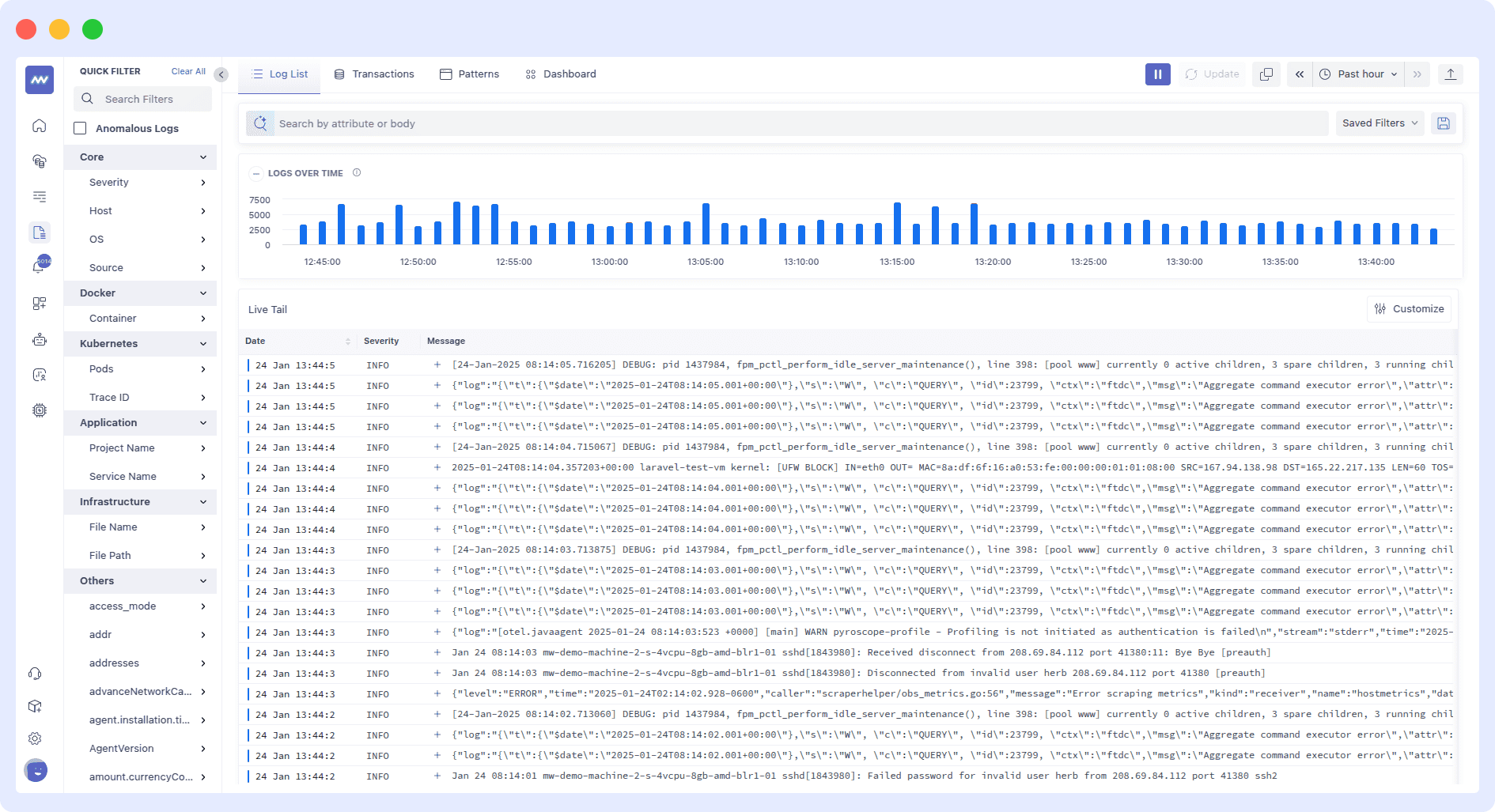
6. Check the log files on your EC2 instances
Checking log files on your EC2 instances is an important AWS monitoring best practice. Log files provide valuable information about your system events, errors, and application performance.
To check log files on EC2 instances, you can SSH into the instance and navigate to the relevant log files.
Collect the following log data:
- Database Logs: To detect slow queries.
- Application Logs: Understand the root causes of application failures.
- AWS CloudTrail Logs: To detect API calls made to the application.
- OS Logs: To identify host-failure reasons.
- Web Server Logs: To capture firewall logs and VPC logs for patterns of access and attacks.
However, manually checking log files can be time-consuming and inefficient, especially in larger environments. That’s where log monitoring tools, such as Middleware, can be useful.
To simplify the process, you can use tools like Middleware to collect log data from multiple sources, including EC2 instances, and provide centralized log analysis.
You can search, filter, and analyze log data, set up alerts and notifications, and quickly troubleshoot issues in your AWS environment.
7. Monitor Costs
Although AWS offers automatic scalability and elasticity to systems, monitoring costs continuously to ensure resource utilization stays within a budget is important.
Here are some tips to keep costs in check:
- Map resources to requirements: Reduce costs by stopping or resizing low-utilization instances, databases, and other resources.
- Locate resource waste: Snapshot and delete low-utilization EBS volumes and idle load balancers to reduce costs. Use low-cost storage tiers for infrequently accessed S3 objects.
- Ensure reliability: Monitor workloads using logs and metrics and set up notifications for significant events and threshold violations.
There are various ranges of AWS monitoring tools (free and paid) to help you monitor your systems. Let’s have a look at them:
Middleware
Middleware is a full-stack cloud observability platform that specializes in complex, multi-tiered applications. It provides comprehensive management of both the application layer and the underlying infrastructure, along with intelligent alerting and visualization features.
AWS CloudTrail
It enables you to track events across your account by automatically recording event logs and activity logs for your services and storing the data in S3.
These logs include critical information such as user identities, traffic origin IPs, and timestamps. While management events can be viewed for free for the last 90 days, data events and insights based on your data are available for an additional fee.
AWS CloudWatch
CloudWatch lets you collect and analyze metrics from various sources.
It consists of two primary parts:
- Alarms: These generate notifications when predefined thresholds are met for individual metrics.
- Events: These enable you to automate actions based on metric values or system changes.
Additionally, CloudWatch provides tools for visualizing metrics and logs, making it easier to monitor (and troubleshoot) your systems.
Datadog
Datadog, a cloud-based monitoring platform, offers real-time visibility into metrics and logs from your AWS infrastructure. It supports a wide range of AWS services and offers advanced features, including anomaly detection and machine-learning-based forecasting.
Dynatrace
Dynatrace is an AI-powered monitoring platform that provides full-stack observability for your AWS applications and infrastructure. It automatically discovers and maps your entire environment and uses machine learning to provide insights and recommendations to optimize performance and reduce downtime.
8. Use AWS Tagging for Resource Organization and Tracking
You can optimize resource management using AWS tags to categorize and track AWS resources based on custom metadata. This way, you can create a standardized tagging strategy across and track resource ownership, environment, and purpose.
To take it up a notch, use AWS services like AWS Resource Groups and AWS Cost Explorer to analyze and optimize tagged resources.
For example, you can use AWS tags to:
- Analyze costs associated with specific resources or projects.
- Identify resources belonging to specific departments or teams.
- Track resources used for development, testing, and production environments.
9. Implement a Centralized Logging Strategy
A centralized logging strategy helps you collect, store, and analyze logs from various AWS services and applications. By using AWS services like Amazon CloudWatch Logs and Amazon Kinesis or third-party tools like Middleware, you can implement log aggregation and filtering, and analyze logs using AWS services like Amazon CloudWatch Logs Insights.
This will enhance visibility into the overall system and application performance, strengthen security monitoring, and accelerate incident response.
10. Conduct Regular Security Audits and Compliance Checks
Regularly conduct security audits and compliance checks to ensure your AWS environment meets the required standards. You can do this using in-house services like AWS IAM Access Analyzer and AWS CloudTrail, and implement remediation and mitigation strategies for identified security risks.
To Conclude
Utilizing appropriate AWS monitoring tools can significantly transform your cloud operations and enable you to:
- Detect cost inefficiencies
- Allocate costs more confidently
- And avoid unpleasant surprises during billing cycles.
However, relying solely on tools won’t solve all monitoring challenges. Implementing the AWS monitoring best practices outlined above and using the right tools are essential to building a solid foundation.
Adopting these practices and tools can help you prevent minor issues from escalating into major (and costly) problems.
Ready to simplify AWS monitoring in 2026? Try Middleware’s full-stack observability platform with built-in AWS best practices – sign up now, it’s free!
What are the top AWS monitoring best practices for 2026?
Essential practices include defining goals, full data collection, automation, alerts, log checks, cost monitoring, tagging, centralized logging, and security audits. Middleware simplifies implementation with AI-powered insights, real-time dashboards, and CloudWatch integration for faster issue resolution.
How do I set up AWS CloudWatch alerts effectively?
Define baselines (e.g., CPU >80%), configure SNS notifications, and use escalation policies. Middleware enhances this with dynamic AI alerts that adapt to trends, reducing false positives by 50%+ compared to CloudWatch’s static thresholds, ensuring proactive responses.
What are the best AWS monitoring tools in 2026?
Leading options are CloudWatch (native), Middleware, Datadog, and Dynatrace. Middleware stands out for cross-platform monitoring (AWS, Azure, GCP), predictive analytics, and unified logs/traces, outperforming CloudWatch in hybrid setups with customizable dashboards and instant root-cause analysis.
Why is AWS cost monitoring important, and how does Middleware help?
It prevents waste from idle resources like EBS volumes, enabling rightsizing and budget alerts. Middleware automates optimization recommendations based on usage patterns, integrates cost data with performance metrics, and cuts expenses more effectively than CloudWatch alone.
How to automate AWS monitoring tasks with Middleware?
Leverage CloudFormation, Lambda, Config, and SageMaker for basics. Middleware takes it further with predictive scaling, event-driven automation across multi-cloud environments, and anomaly detection, slashing manual efforts and downtime versus CloudWatch limitations.
