When a production system collapses at 3 AM, the immediate reaction is to restore it. You bring the service back online, traffic is restored, and the incident is closed. But then it reoccurs, time and time again. This is the cycle, as we tend to treat visible issues rather than discover what was actually broken. A database timeout, a memory leak, a cascade failure; these are effects, not causes. Addressing surface issues without identifying their root causes or failing to catch deployment issues early can lead to recurring outages and wasted effort.
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) helps identify the cause of an incident rather than treating its symptoms. It allows teams to discover what really went wrong, ensure that it does not happen again, and have more stable systems.
In this post, we will describe the concept of Root Cause Analysis, its relevance in engineering teams, and how to approach it. We’ll also look at how observability platforms, such as Middleware, can accelerate and improve RCA accuracy.
✅Also Read: How to Detect API Latency and Improve Performance
What is Root Cause Analysis (RCA)?
Root Cause Analysis is a technique used for identifying the fundamental cause of a failure or incident. It does not only stop at the immediate indicator itself but digs to find out what actually caused it.
Practically, this implies not stopping at the apparent mistake but tracing the problem through layers of dependencies until the root is identified. It is the distinction between knowing “what broke?” and “why did it break?”
This might seem like troubleshooting, which is usually the starting point when something is wrong. Troubleshooting, however, is geared toward restoring things to their normal working state as quickly as possible.
For example, a crashed service can be restarted and resume normal operations; however, this does not answer the question of why the service crashed in the first place. RCA, however, goes a step further to identify the root cause, which could be a memory leak, an improper configuration, or an unhandled exception.
Why RCA is Critical in Modern Software Systems
Modern systems are complex. They are based on distributed architecture, microservice, APIs, and cloud infrastructure. Failure of a single component can affect multiple services and end users within a few seconds. When it occurs, teams often have thousands of logs and alerts from various tools, making it challenging to determine when the problem started.
RCA brings order to this chaos by helping teams:
- Address the areas of weakness before they become repetitive issues.
- Enhance system reliability with informed corrections.
- Lessen downtimes by fixing the underlying problem more quickly.
- Strengthen communication between teams during incident reviews
Root Cause Analysis is the key to building resilient, predictable systems in the software environment.
👉 Discover how centralized log management and infrastructure monitoring in Middleware improve reliability across distributed systems.
Why Root Cause Analysis Matters
Root Cause Analysis shifts teams from reactive firefighting to proactive prevention.
Instead of repeatedly fixing the same issues, RCA helps you eliminate recurring problems at their source. By knowing the causes of problems, the teams will be able to spend less time fixing issues and more time on enhancing the entire system.
When RCA is effectively carried out, teams experience such benefits as:
- Reduced recovery times (MTTR): A well-organized process will help identify and address the actual problem more easily, thereby enabling systems to recover more quickly.
- Less repeat problems: Finding the real root cause of a failure assists in preventing the occurrence of the same issues in future updates or deployments.
- Optimized cost: Reduced unexpected downtimes and minimum-minute repairs will make time and money more effective.
- More dependable systems: A solution to the root cause of a recurring problem is a system that is more stable, resilient, and scalable.
- Faster troubleshooting: RCA eliminates guesswork by providing evidence, allowing engineers to focus on what is actually wrong rather than false leads.
- Reduced fatigue due to alertness: The teams will be better equipped to respond because noise filtering will help them stay focused and react only to meaningful alerts.
- Continuous enhancement: Each RCA contributes to what the team is familiar with, and such information will shape the improved designs, greater monitoring, and smarter functioning in the long run.
How to Conduct Root Cause Analysis
Conducting a successful Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is not about what broke, but why it broke and how to prevent it in the future. Teams must follow a systematic approach that begins with problem definition and concludes with permanent prevention. Although the specifics may differ across organizations, the majority of RCAs follow the general steps:
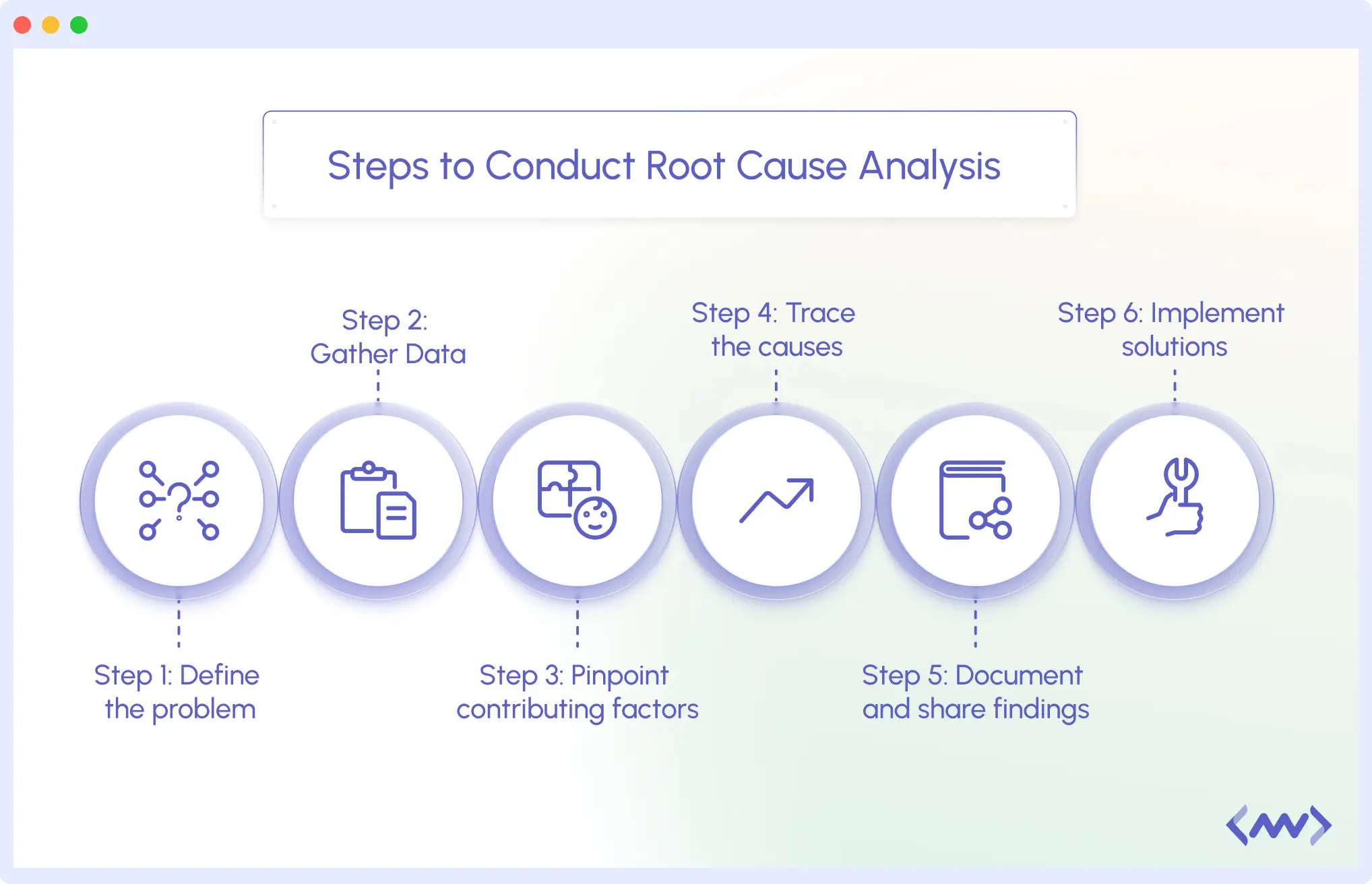
1. Define the Problem
Accurately describe the event, its scope, and its impact. This phase depends on thorough and unbiased data collection. A good problem statement defines the incident objectively without assuming a cause. It should answer:
- What failed or degraded
- When it started and ended
- Which users or services were affected
- What issues were observed?
2. Gather Data
Then gather all data that may be useful, including the incident log, metrics, traces, deployment history, and configuration changes. Examine components like:
- Application logs and error messages
- System metrics such as CPU, memory, disk, and network usage
- Distributed traces showing request paths
- Recent deployments or infrastructure updates
- Alerts that fired before or during the incident
This process can be facilitated using observability tools such as Middleware, which can consolidate data across services into a single view.
3. Pinpoint Contributing Factors
After collating the data, search for all factors that might have contributed to the failure. A single problem does not trigger most incidents; most occur due to a combination of factors, including system dependencies, configuration errors, and human error.
4. Trace the Root Cause
From that list of contributing factors, identify the single underlying issue that caused the event. Methods such as the 5 Whys or Fault Tree Analysis can be used to identify the root cause of signals and separate the actual cause.
5. Implement solutions
After identifying the root cause, apply a specific fix. This could include code updates, configuration changes, or infrastructure updates. Do not use hasty patches that temporarily fix the service but do not address the problem at its root.
👉 Want to try it yourself? See how to set up GitHub Integrations and connect Middleware Ops AI with your repo in minutes.
6. Document and Share Findings
After all the issues are sorted out, take time to write down the whole process of what went wrong, why it went wrong, how it was corrected, and the preventive measures.
A good RCA report should consist of:
- A summary of the incident
- An elaborate chronology of events.
- The root cause explanation
- Repairs and preventive actions.
This knowledge sharing will enable other teams to learn and not repeat the same mistakes in the future.
How Middleware Simplifies Root Cause Analysis
Manually conducting RCA across distributed systems involves juggling multiple tools, matching information across various sources, and reassembling a timeline from fragmented data. It is a lengthy process that is likely to overlook important details.
Here are some of the ways Middleware can help streamline RCA by providing unified observability, AI-driven insights, and end-to-end visibility.
Unified Observability for Complete Visibility
One of the biggest challenges in RCA is the fragmentation of data. Middleware fixes that combine logs, metrics, and traces from containers, databases, servers, and major cloud providers such as AWS, GCP, and Azure into a single view.
You can then automatically trace a user’s request in the browser to the failed backend service or database. You do not have to switch between tabs or rely on context to guess what you are looking at; all that you require is in one view
Key RCA Features
Beyond data consolidation, Middleware provides intelligent tools that accelerate each step of the RCA process.
Unified Timeline
Your logs, metrics, traces, and deployment events are all displayed on a single timeline. It means you will instantly be able to see when a deployment occurred, when errors began, and how your system metrics responded, without manually constructing a timeline yourself.
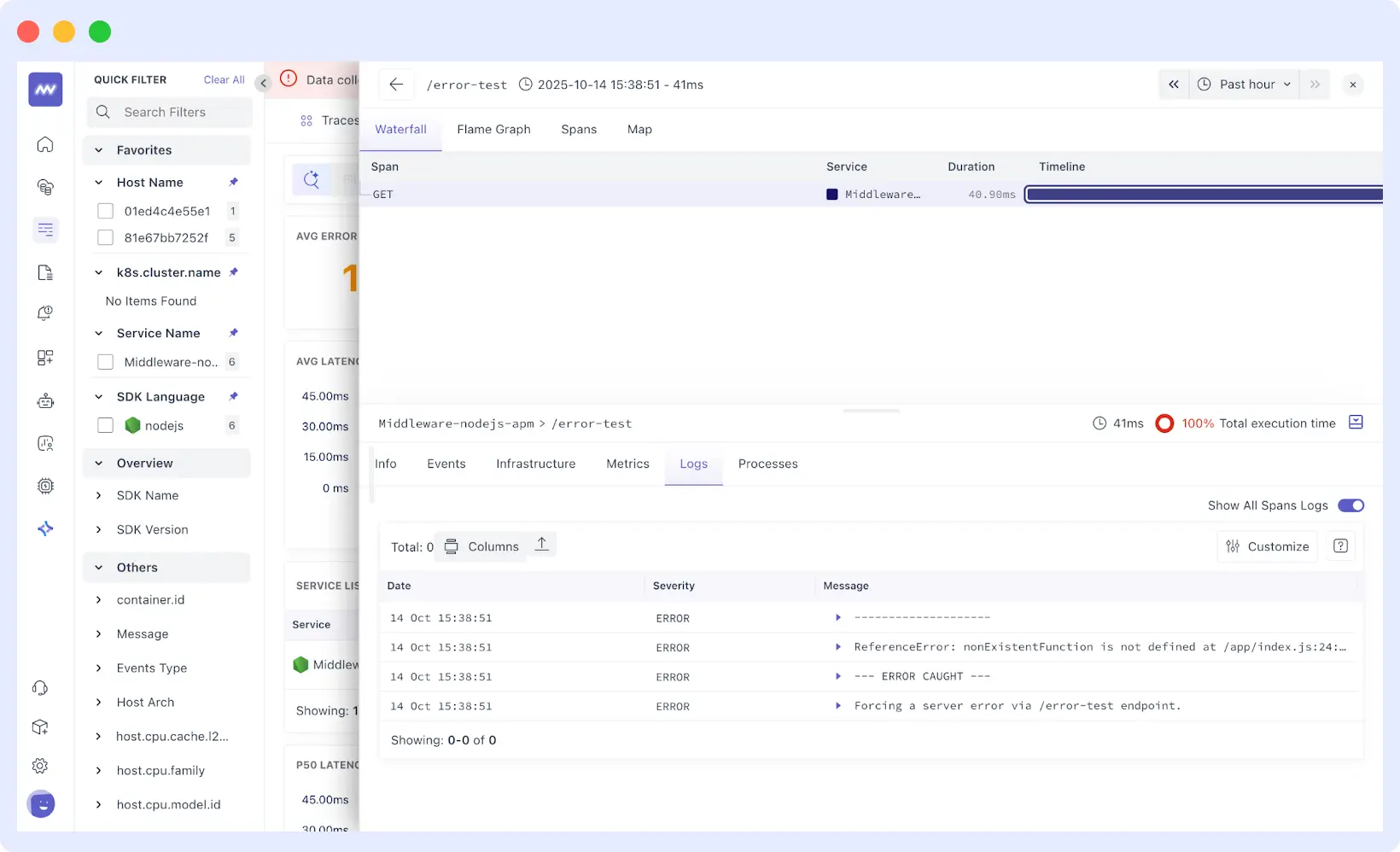
Interactive Correlation
Hover over any metric spike to see what was happening across all other systems at that exact moment across CPU, memory, network, database connections, and more. This cross-reference capability helps connect visible causes to underlying issues without having to jump between graphs manually.
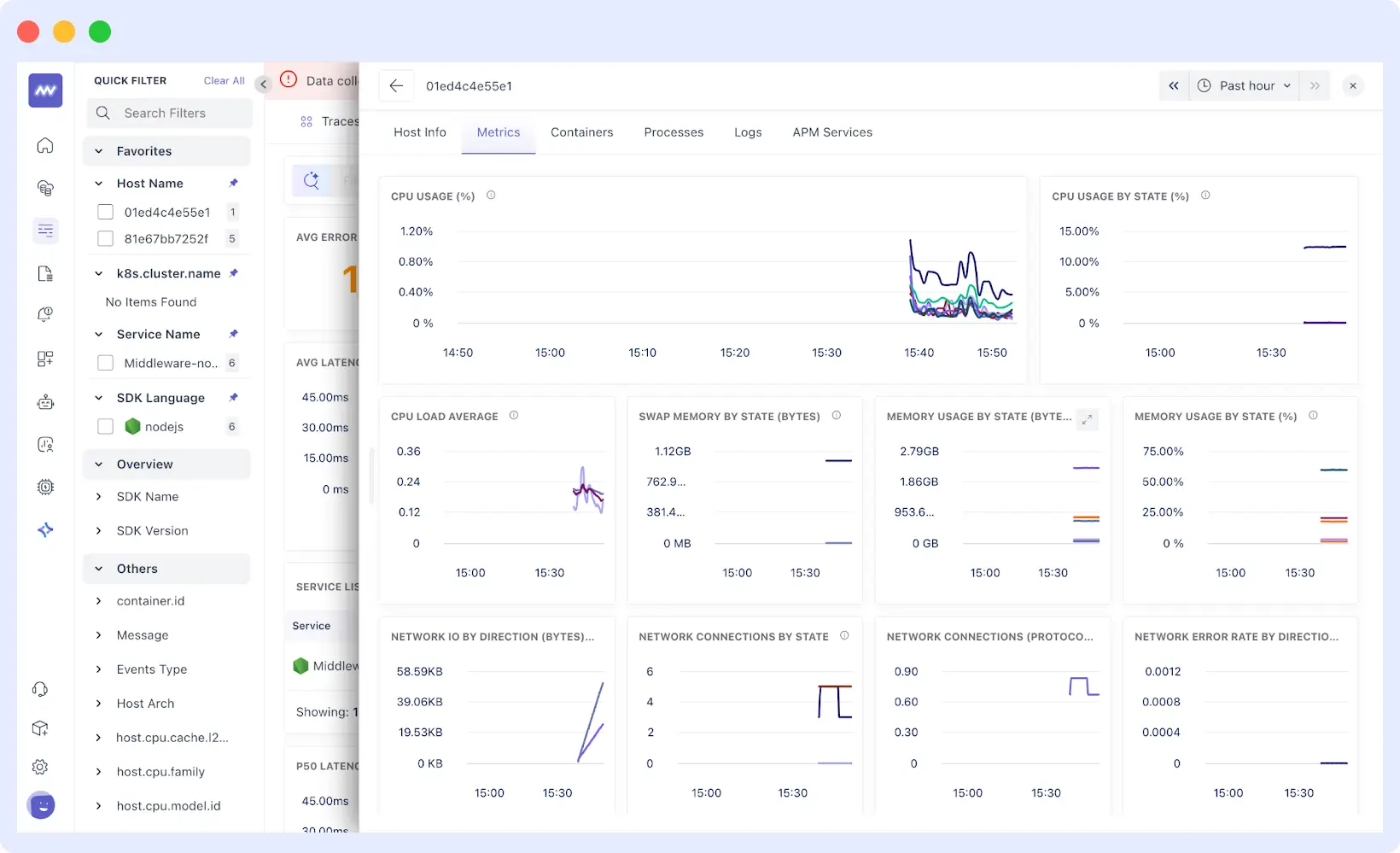
Distributed Tracing
Middleware’s distributed tracing follows a request through your entire microservices architecture to pinpoint precisely where latency was introduced or where an error originated. Each trace connects to related logs and metrics, giving you full context without switching tools.
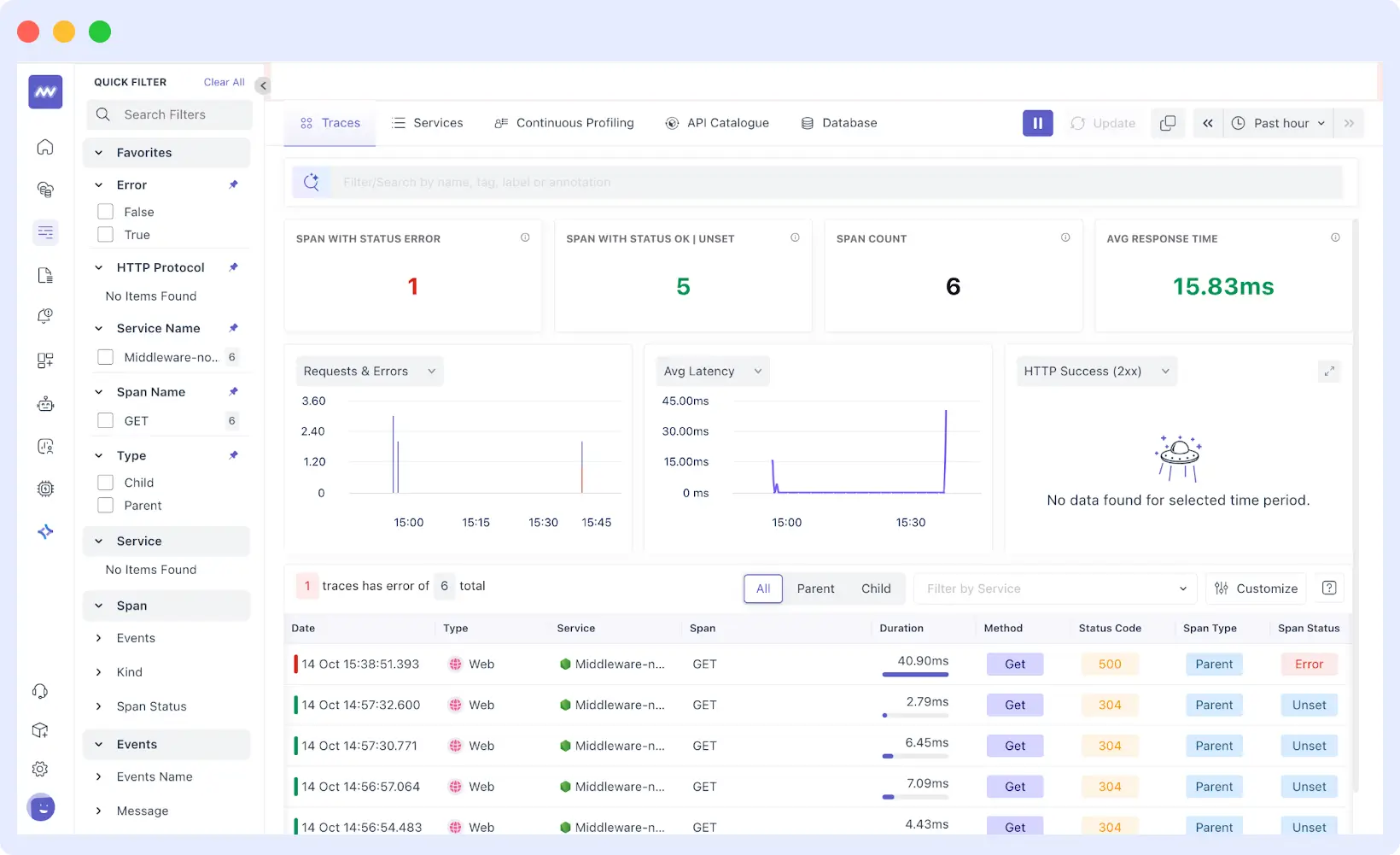
AI-Powered Root Cause Detection with OpsAI
At the core of Middleware’s RCA capability is OpsAI, an intelligent diagnostic engine that applies machine learning to detect, analyze, and correlate issues across distributed systems. OpsAI uses large volumes of logs, metrics, and traces to identify the likely starting point of a problem, rather than manually searching them.
👉 Learn more about OpsAI by Middleware, the AI-driven engine that detects and correlates system-wide issues automatically.
It goes beyond basic error reporting by providing detailed insights that developers can act on immediately. Each error is presented with complete context, including the error type, message, and stack trace, which makes it easier to understand what went wrong. OpsAI can also pinpoint the exact section of code, file, or configuration involved, reducing the time engineers spend searching for the cause.
Over time, OpsAI becomes more effective as it learns from past incidents. It builds awareness of recurring patterns, helping teams predict and prevent similar issues before they escalate.
⚡ Want to see how OpsAI detects root causes in your environment? Request a Demo
Correlation of Frontend and Backend Data
Middlewares link frontend and backend insights to achieve end-to-end visibility. You can trace an issue through the user’s browser, the network, and into the backend service or database that is causing the problem.
Digital Experience Monitoring
Middleware displays the actual effects of incidents on end users with real user monitoring (RUM) and synthetic checks.
Also Read: Synthetic Monitoring & Tracing for Proactive Incident Detection
This helps teams verify whether a backend issue is impacting performance or customer experience.
👉 Explore how Digital Experience Monitoring (DEM) helps teams measure and enhance real user experiences.
Automated Correlation and Contextual Insights
Middleware automatically links related events across services to provide contextual insights. For example, if a latency spike in a database causes frontend timeouts, Middleware correlates these events and surfaces them together.
This eliminates guesswork and makes it easier for engineers to move from detection to understanding within minutes.
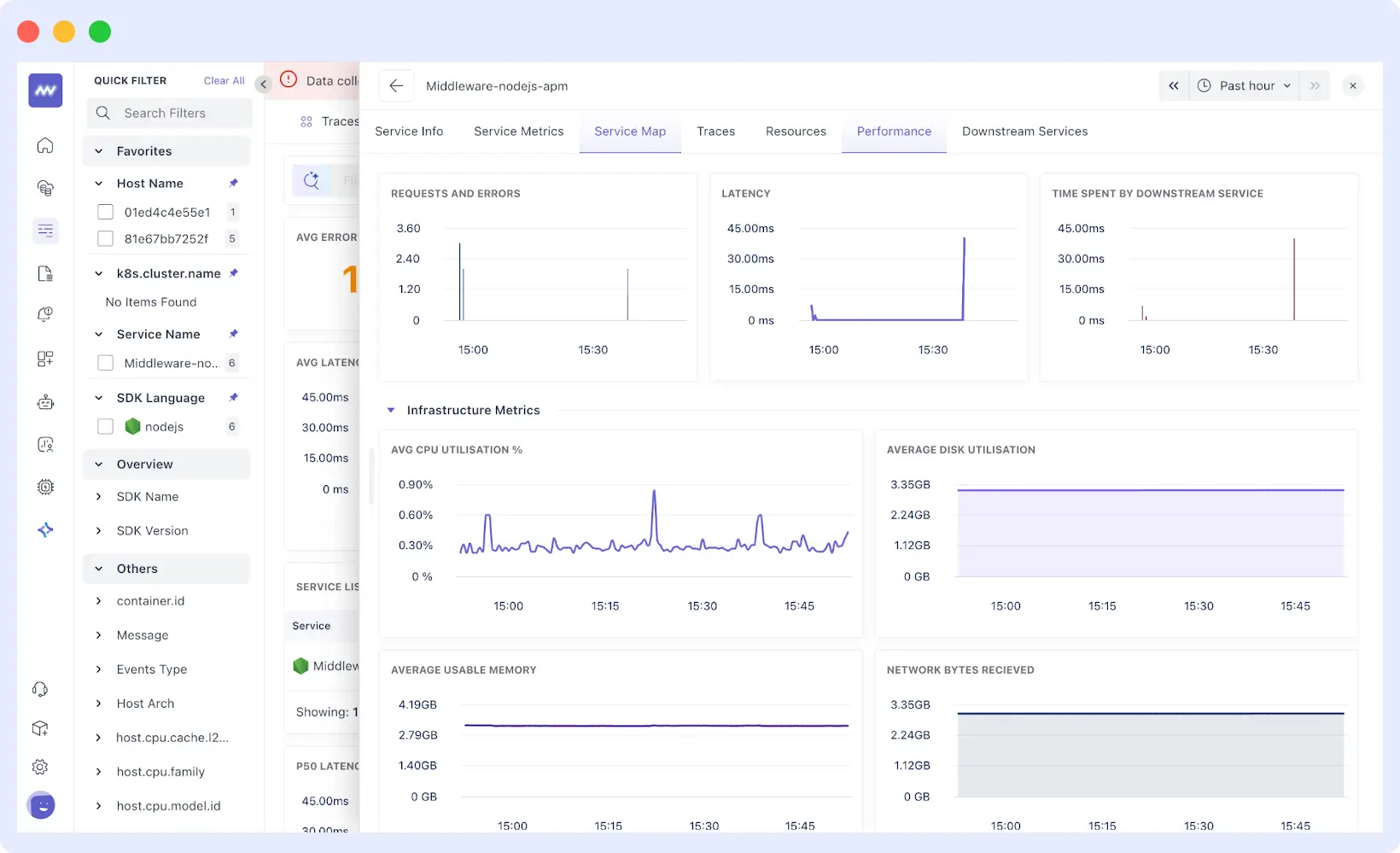
Support for Diverse Data Sources
A broad range of data sources can be ingested, including containers, databases, and other cloud systems such as AWS, GCP, and Microsoft Azure. This provides a complete view of the entire stack, and problems will not be concealed in unmonitored systems.
Root Cause Analysis becomes a quick, data-driven, and intelligent operation with Middleware, rather than a time-consuming, manual process.
Why Teams Choose Middleware for Root Cause Analysis
Unlike traditional monitoring tools that alert you when something breaks, Middleware is purpose-built for modern distributed systems where incidents involve multiple services and complex dependencies.
Key Differentiators:
AI-Driven Root Cause Detection
While other tools show you what’s broken, OpsAI tells you why. It analyzes patterns across your entire stack to surface probable root causes, not just effects, automatically.
Unified Observability
See logs, metrics, traces, and deployments on a single timeline. No more switching between Grafana for metrics, Splunk for logs, and Jaeger for traces. Everything correlates automatically.
Instant Setups
Pre-configured dashboards for containers, databases, AWS, GCP, and Azure deliver value immediately. No lengthy instrumentation or custom configuration required.
Faster MTTR by 60-80%
Teams report resolution times dropping from hours to minutes. Middleware eliminates the manual correlation work that consumes most incident response time.
Learn more about how Middleware improves error tracking and cuts down MTTR ⏱️ for modern engineering teams
Built for Microservices and Cloud-Native
Native support for Kubernetes, serverless, and distributed architectures. Monitor ephemeral containers, dynamic scaling, and service mesh complexity without additional configuration.
What Engineering Teams are Saying About Middleware
“We use Middleware.io to monitor our infrastructure. The integration takes minutes and it comes preconfigured with very nice and detailed dashboards. It’s powered by AI and saved a lot of time for our engineers on troubleshooting and fixing hidden bottlenecks on our AI engine.”
Ashot, Cloudchipr
“The AI-powered insights have helped us identify and resolve issues faster, resulting in stellar uptime and increased customer satisfaction for Fortune 500 customers.”
Tatevik, Activeloop
From startups to enterprises, teams use Middleware to shift from reactive firefighting to proactive root cause analysis, reducing MTTR and building more reliable systems.
Conclusion
Root Cause Analysis is not just a post-incident activity but it is an ongoing activity that reinforces the manner in which teams develop, run, and sustain software systems. Engineering teams can shift to prevention by not merely being reactive to failures but rather seeing through the cracks and the real cause of failure.
We’ve seen how Middleware simplifies this process by unifying observability data, providing intelligent insights through OpsAI, and reducing the time spent finding and fixing issues. With Middleware, RCA becomes faster, more precise, and more actionable.