Bugs found at the last minute are annoying and delay deployments. Testing late in development usually causes it. Shift-left testing aims to prevent issues by catching them early in the development process.
For a long time, that was just how software teams worked: build first, test later, ship when it’s stable. That made sense when release cycles were slow. But today, updates are done regularly, so waiting until the end to test only slows everything down.
Shift-left testing changes that. Teams include testing in planning, design, and development. Early testing reduces surprises.
🧠Shift-left testing moves testing earlier in the software development lifecycle, helping DevOps, QA, and developers detect issues sooner, speed delivery, and cut costs.
What is Shift-Left Testing?
Shift-left testing is a software testing strategy that moves testing earlier in the SDLC to detect bugs sooner and improve product quality. It focuses on identifying errors early in the development process to prevent rework, reduce costs, and expedite delivery.
Traditional software development begins with building and then notifying the QA team to test. The QA team informs developers of any bugs that need to be fixed. The process continues until everything works well. It takes forever and is frustrating.
🎯According to the 2025 State of DevOps Report, teams adopting shift-left testing reduce post-release defects by nearly 40%.
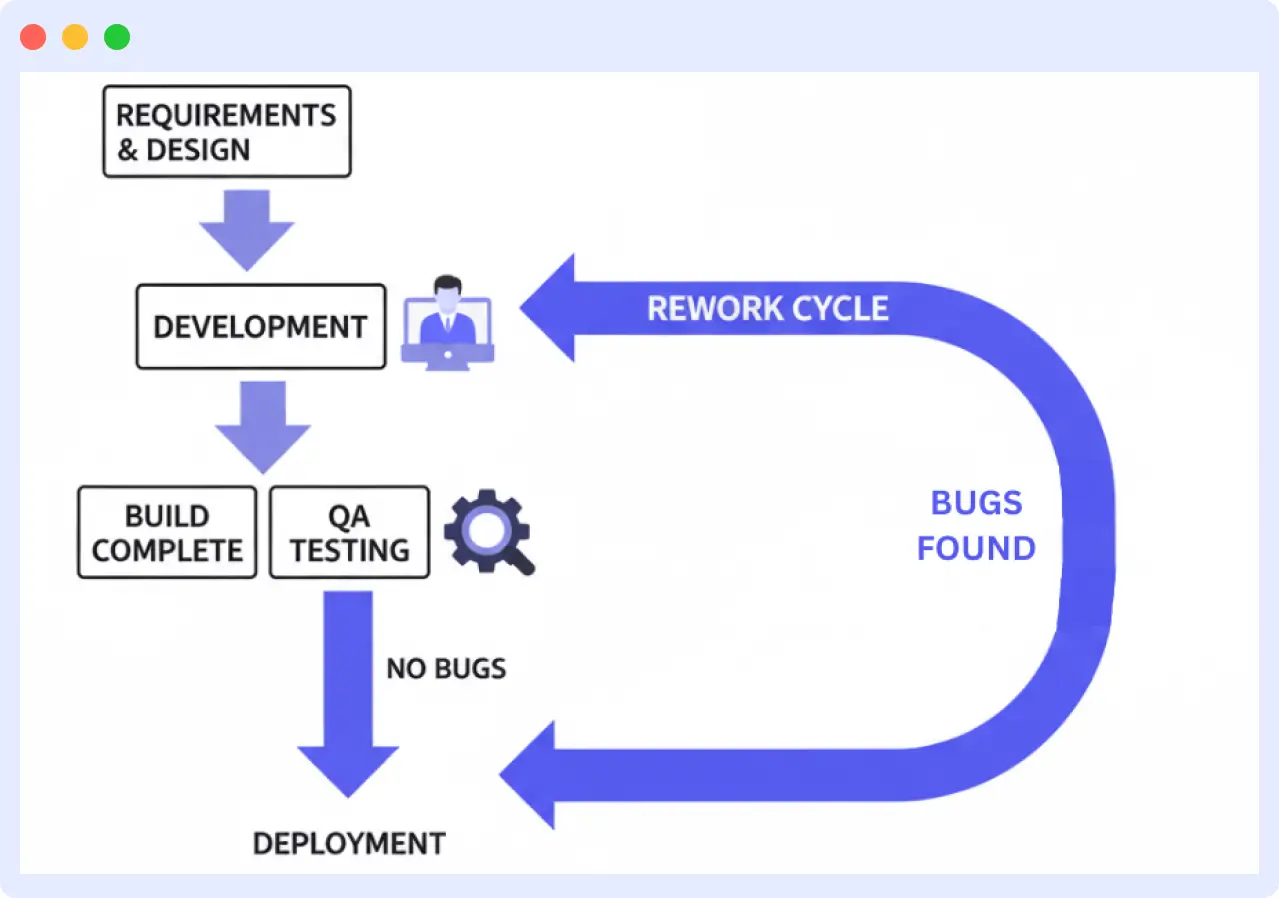
Shift-left testing works differently. From the start, developers, QA, and DevOps collaborate. It helps find issues early, from requirements to code and integration.

Instead of resolving problems late, shift-left testing finds them early. It saves time, reduces rework, and encourages smooth releases. Any modern DevOps team seeking continuous delivery should use this approach.
Types of Shift-Left Testing
The parts of software being tested determine the type of shift-left testing to carry out. They include:
- Unit Test: Enables developers to test individual components and functions early, ensuring they work as expected in isolation.
- Integration Test: Checks if units work together seamlessly and detects service or API communication issues.
- API Test: Verifies API reliability, error handling, and data exchange accuracy. APIs connect application components. API testing verifies that these connections send and receive data correctly, manage errors, and perform reliably under diverse conditions.
- UI Test: Examines user interface functionality and usability. Fast, automated UI tests help validate user flows after each code change. UI testing examines the app’s appearance and behavior. Button, form, and navigation functionality are tested. Fast automated UI testing helps verify user flows following code modifications.
📈Pro Tip: Automating these tests in your CI/CD pipelines makes shift-left testing faster and more scalable.
Benefits of Shift-Left Testing
Shifting testing to the left means building strong software from the start as well as finding flaws early.
Here are some reasons to follow this development method:
Finding Bugs Early
“The sooner you detect a bug, the easier it is to fix.”
In shift-left testing, early bug detection reduces rework and accelerates the release cycle, a key component of every modern DevOps testing strategy.
Traditional testing leaves many issues till the end of development. By then, errors in multiple components make fixes more challenging and time-consuming.
💡To explore how modern teams detect bugs early in production too, read our guide on debugging live production issues
Shift-left testing can identify bugs in the design or development phase. Quick feedback helps developers identify and fix errors while they are still working.
Unit tests should be included for every new feature, enabling developers to detect and resolve issues quickly. If they wait, the issue will possibly spread making it more difficult to find.
Early automated testing enhances reliability, reduces costs, and enables the development of higher-quality software more efficiently.
Reduced Cost of Fixing Bugs
Bugs can cost 10x more to fix after release than during development. Late-stage bugs affect multiple features, require extensive retesting, and may impact production users.
Shift-left testing prevents that from happening. Early bug detection lets teams focus on product improvement rather than bug hunting. It saves time, costs, and enhances quality.
Improved Software Quality
Early and frequent testing makes software more reliable. While building the system, testing each part reduces hidden problems.
Additionally, shift-left testing promotes good coding practices. Early quality consideration helps developers build cleaner, more maintainable code.
⚙️Shift-left testing goes hand-in-hand with proactive issue detection. See how Middleware helps teams detect and resolve DNS issues before they impact users.
Better Collaboration
Early in the development process, shift-left testing brings together testers and developers. They share quality responsibility instead of operating in silos.
Collaboration speeds feedback, reduces misconceptions, and streamlines releases. Team trust grows when everyone can see test results, follow progress, and act quickly.
For instance, prior to development starting, QA will examine user stories and identify test cases during sprint planning. This will help developers avoid going back and forth.
How to Implement Shift-Left Testing
Implementing shift left-testing is simple. It only means bringing testing closer to development. To apply shift-left testing effectively, align your QA and DevOps practices early in the development cycle. Follow these core steps:
Test During Requirements Gathering
Development doesn’t stop testing. When getting requirements, testers should analyze user stories and acceptance criteria early. This helps identify gaps, conflicting expectations, and risks before the development phase.
If a tester notices that a requirement doesn’t define how the system should respond in an edge scenario, they can clarify promptly, saving time.
Use Automation Early and Often in CI/CD
Keeping up with early testing requires automation. Write automated unit, integration, and API tests after building new features.
💡With Middleware, you can detect API latency in real time, analyze traces, and resolve bottlenecks before they affect performance.
CI pipelines can automate new code tests to prevent bugs from occurring. Fast feedback while adding or changing code prevents old bugs from resurfacing.
Make Quality a Team Effort Across Dev & QA
All individuals involved in developing, testing, and owning the product should prioritize quality from the outset.
Teams that identify risks, provide early feedback, and code review together make fewer mistakes. Instead of waiting for testing, developers can partner with testers throughout feature development to test as they build.
Use Static Code Analysis and Linters For Early Detection
Static code analysis and linters find bugs before execution. They save testing time by checking code for bugs, syntax errors, security risks, and bad practices as you write.
ESLint for JavaScript and SonarQube can detect bad code and sluggish performance. This keeps code neat and reduces the need for debugging.
Adding Testing to CI/CD Pipelines
Use shift-left testing in your CI/CD pipeline to enhance efficiency. Every time new code is published, automated tests are triggered, enabling teams to catch errors before they reach production.
With tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or GitLab CI, you can set up automated builds, run tests for every change, and get instant feedback.
This continuous testing keeps the codebase healthy and ensures that no new bugs slip through unnoticed.
By integrating testing into planning, coding, and CI/CD pipelines, teams can effectively shift left, improving delivery speed and product stability.
How Does Middleware Support Shift-Left Testing?
Middleware simplifies shift-left testing by giving complete observability and performance insights across all development stages, from local testing to production readiness. Additionally, it serves as both a shift-left observability platform and a DevOps testing enabler, making early-stage debugging effortless.
Middleware provides developers and QA engineers with visibility and insights from the start of the software development lifecycle, helping teams execute shift-left testing. Here’s how:
Real-Time Visibility From Early Stages
Tracking local development and staging across several environments is difficult when shifting left. This is simple with Middleware. With Middleware’s real-time monitoring and observability, teams can track logs, metrics, and traces during early testing phases.
Even in the early phases of testing, teams can track data, logs, traces, and performance as soon as new code executes. This early access enables developers to make decisions based on data long before the release, observe how their code runs, and identify errors more quickly.
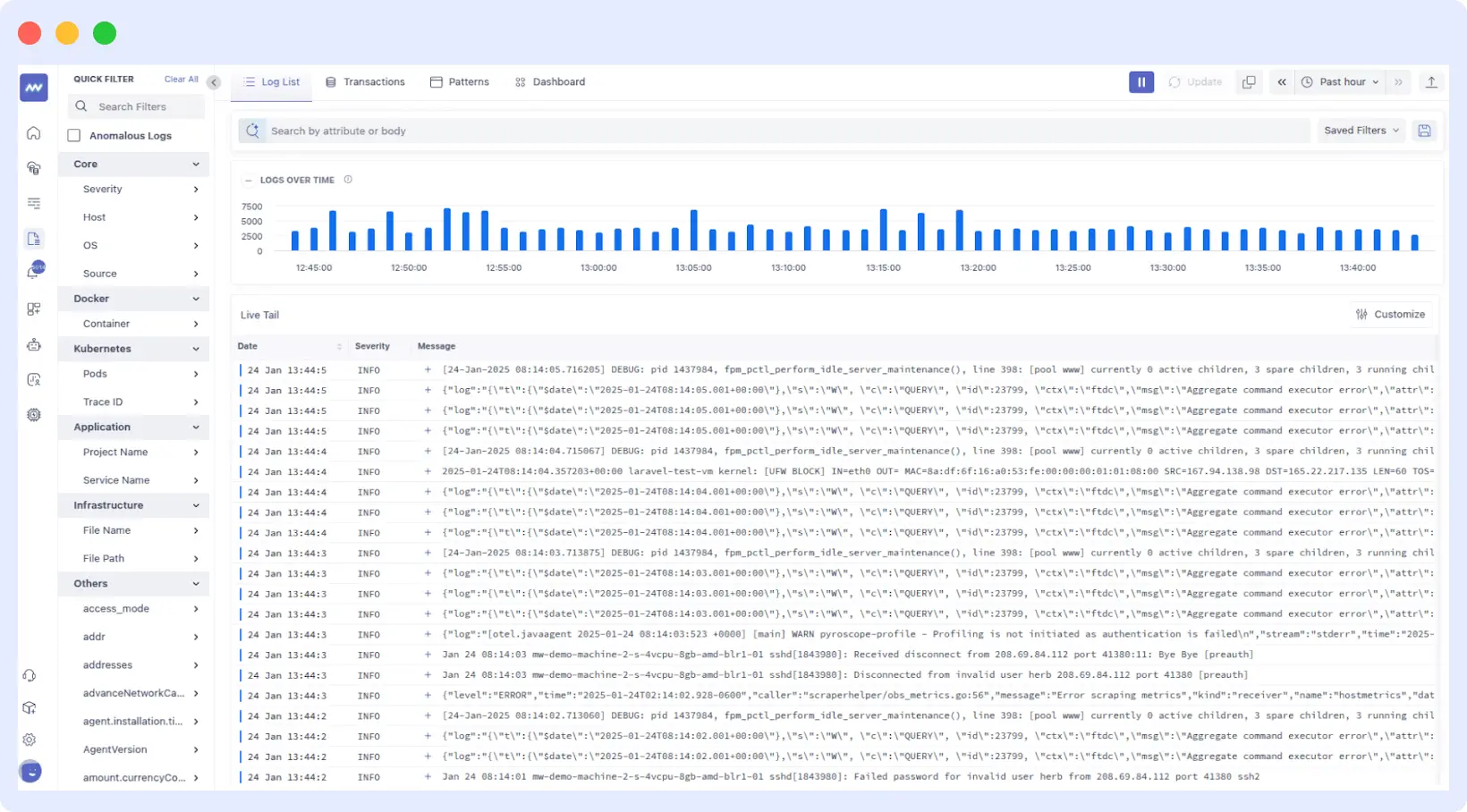
Middleware will indicate whether deploying a new feature to a test environment results in improved response times or increased resource utilization. This lets developers resolve performance issues before production.
Middleware gives developers early feedback on code performance, resource usage, and latency, enabling proactive testing before release.
Detect Issues on Time
Middleware’s AI-powered alerts and real-time insights enable faster detection of early issues compared to traditional QA monitoring.
Having the proper insight at the right time is also necessary for catching issues early. Middleware helps teams detect anomalies, failed dependencies, and error spikes the moment they happen.
For example, if a service fails during integration tests, Middleware flags it instantly. It helps developers debug with complete context, with logs, metrics, and traces all in one place.
Middleware also notifies developers when issues arise through real-time alerts and AI-powered insights. It might be a sudden increase in latency, high CPU usage, or a failing API call.
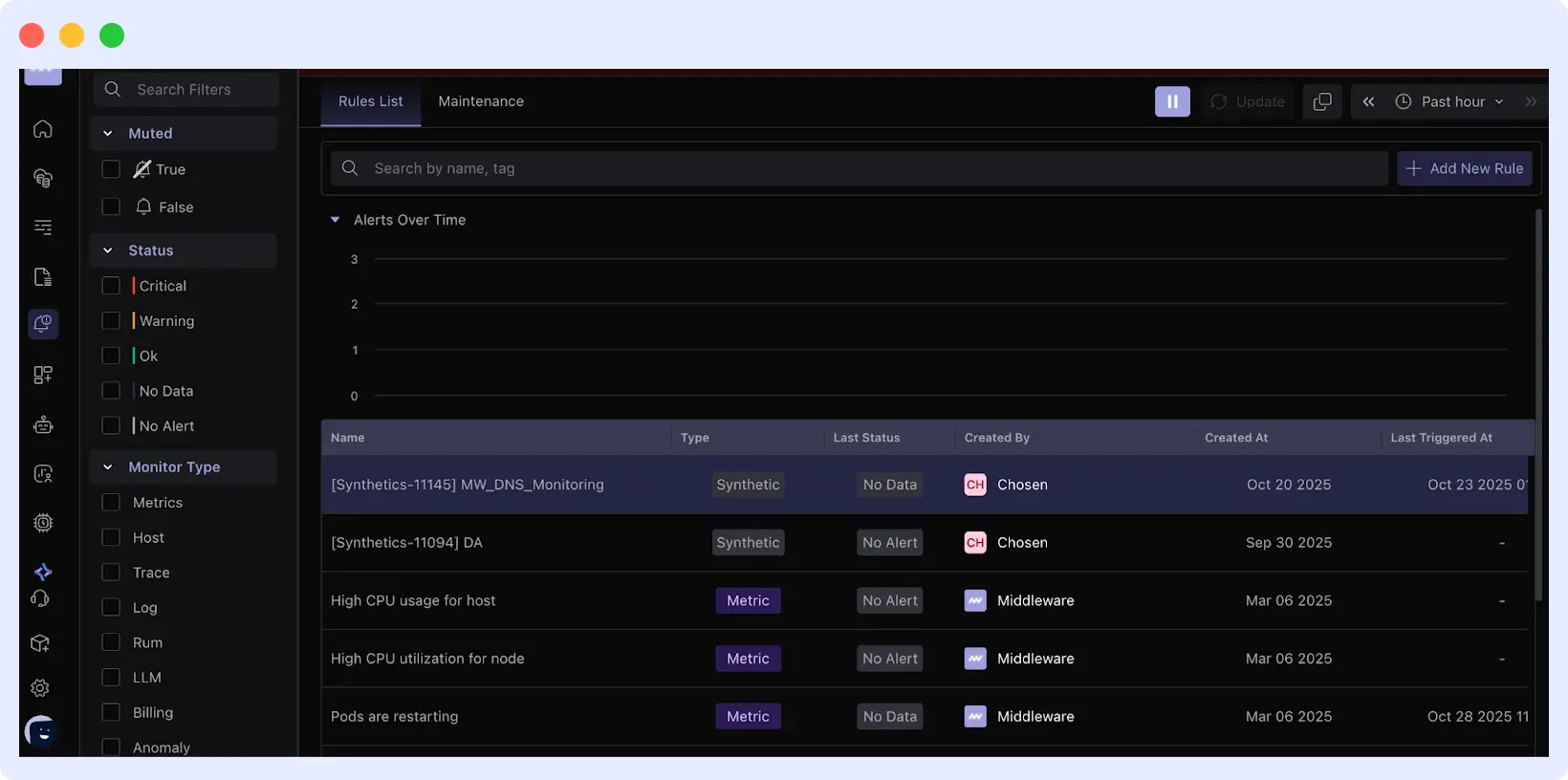
Teams can act quickly without QA or production monitoring.
Teams can identify performance anomalies, failed APIs, and resource spikes immediately, thereby reducing the mean time to resolution (MTTR).
Integration with CI/CD Pipelines
Middleware integrates seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines such as Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and GitLab CI to ensure continuous testing and observability at every deployment stage.
You can test and monitor your application from development to deployment with Middleware. It works great with your CI/CD workflow.
Integrating Middleware with your CI/CD platforms allows you to monitor each build, deployment, and test run effortlessly. In other words, before going live, any modification to the code is thoroughly examined for any performance or reliability issues.
Every build and deployment is automatically tested, monitored, and validated before being deployed to production.
Unified observability across the SDLC
Middleware provides unified observability across the SDLC, enabling shift-left and shift-right testing continuity.
Shift-left testing is a continuous process. Middleware enables teams to view the entire SDLC, facilitating easier collaboration.
It unifies logs, metrics, traces, and events across development, staging, and production environments. Developers, testers, and DevOps professionals can easily identify and resolve issues.
Unified observability empowers Developers, QA, and Operations Teams to collaborate seamlessly across development, staging, and production environments.
How Trademarkia Reduced Time to Resolution by 20% with Middleware
Trademarkia, a leasing trademark search platform, sought to upgrade its infrastructure and boost developer efficiency, but its old setup had poor issue detection and restricted visibility. Their observability tools were complicated and lacked real-time log monitoring. Developers often had to wait to find errors.
Everything changed for Trademarkia when it adopted Middleware’s full-stack observability platform. Trademarkia’s engineering team utilized Middleware’s unified platform to monitor proactively and test microservices during development.
- They saw microservices logs, traces, and metrics in real time.
- Developers can identify and correct bugs during testing and early deployment.
- Automated notifications and Slack integration enable the team to work faster and resolve errors before they become production issues.
What did they get?
- 50% reduction in alert noise
- 20% faster Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR)
- 25% improvement in developer productivity
Trademarkia introduced Middleware early in its development process, making testing and debugging proactive and continuous.
✅Result: Faster debugging, reduced alert noise, and measurable improvement in developer efficiency prove how observability drives shift-left success.
Conclusion
Reliable software is built by shifting testing left. Early, automated, and collaborative testing improves delivery speed and software quality.
Middleware makes this process even easier. With real-time visibility, automated alerts, and full-stack observability, your team can detect issues early, resolve them quickly, and ship with confidence.
Try Middleware for faster bug detection.
🧭Ready to accelerate your DevOps testing strategy? Try Middleware full-stack observability to test, monitor, and deliver with confidence.
FAQs
How does shift-left testing improve software?
Early detection keeps software cleaner and more stable by making bug fixes cheaper and easier.
What types of tests are included in shift-left testing?
Shift-left testing includes unit, integration, API, UI, and automated tests performed early in the software development lifecycle. These tests help detect bugs in code, APIs, and user interfaces before release. Teams also use static code analysis and CI/CD automation to ensure faster feedback, higher quality, and fewer production issues.
What challenges can teams face with shift-left testing?
Getting everyone to test early and setting up automation tools can be challenging at first.
What is the difference between shift-left and shift-right testing?
Shift-left focuses on testing early in development. Shift-right happens after release to monitor software in production.
How does Middleware support shift-left testing?
Middleware connects with CI/CD, providing real-time visibility and helping teams identify and resolve issues.
Is shift-left testing suitable for agile teams?
Yes. Agile teams benefit from shift-left testing because it aligns with iterative development, ensuring faster feedback and reduced rework in each sprint.
What are the best tools for shift-left testing?
Tools like Middleware, Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and SonarQube enable automation, visibility, and performance testing early in the SDLC.



