Whether you’re a DevOps engineer, a data analyst, or someone who runs a business that produces and uses data sets, you need to know about cloud analytics. Cloud analytics is a part of the cloud computing technology stack that helps businesses make informed decisions using data visualization in real-time. Now let’s go beyond cloud analytics hype and get down to brass tacks. This article will cover key components of cloud analytics, including its cost, types, and benefits for individuals, businesses, and organizations.
What is Cloud Analytics?
Cloud analytics refers to storing and analyzing data on vendor-managed infrastructure to extract actionable business insights. Cloud analytics allows businesses to process large data sets in a more scalable, secure and affordable manner. The primary purpose of cloud analytics is to allow companies to view their data in real-time, understand the trends and make business decisions based on the insights gained from the data.

Cloud analytics unifies diverse heterogeneous data sets so that analytics can be performed globally on a single data lake. This processed data can be used for various purposes such as fraud detection, customer churn analysis and forecasting revenues. Cloud analytics tools are typically used to analyze large amounts of unstructured data, including text, images, audio and video file data, that’s difficult to analyze using traditional BI solutions. Cloud analytics tools help businesses make sense of this data by providing visualizations and interactive dashboards that allow them to explore their data in new ways.
Types of Cloud Analytics
Cloud analytics is a subset of business intelligence (BI), but it has a more specific focus. While traditional Business intelligence uses data from multiple sources to help businesses make better decisions and improve operations. Cloud analytics focuses specifically on cloud computing as a source of data and the analysis of that data. When it comes to cloud computing market domination, AWS remains in the first place with a 33% share, followed by Microsoft Azure with 16%. Cloud analytics can be broken down into three categories:
1. Public Cloud
Public cloud analytics refers to analyzing data stored on servers available to anyone with an internet connection. This means anyone with access can view or manipulate the data stored on these servers. Still, there are also many advantages for businesses that utilize public cloud computing services such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
2. Private Cloud
Private cloud analytics refers to analyzing data within a private network that isn’t accessible from outside networks like the Internet or from other locations where people may have access. This type of network is often referred to as an intranet because it connects computers within a single company or organization.
3. Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud refers to a combination of private cloud and public clouds such as Amazon Web Services (AWS). Hybrid clouds allow businesses to take advantage of the benefits of both models while minimizing their drawbacks. For example, a company may use public cloud storage for backup purposes but keep their core systems private cloud for security reasons.
How does cloud analytics work?
Vital elements of cloud analytics like data sources, data models, processing applications, computing power, analytic models and sharing or storage of results are provided by a cloud service provider (CSP).
The CSP will provide you with access to these resources through software application programming interfaces (APIs), which allow you to create your custom software applications or use pre-built tools from the CSP’s marketplace or library.
Cloud analytics involves using various cloud-based tools and services to perform complex analyses on your data. The critical elements of cloud analytics include:
- Data sources – Data sources are defined as locations where the database tables reside and they can include both structured data (such as customer information) and unstructured data (such as social media posts).
- Data models – Cloud analytics applications typically require you to define a schema for your data to be adequately analyzed. You can use any number of different tools, such as SQL-based databases or NoSQL databases. The schema defines how individual pieces of information are related to one another.
- Processing applications are software programs that perform calculations on the raw data stored in your chosen data model. For example, if you want to analyze AWS cost spending over time, you would need to run SQL queries against your AWS account history database to generate a report containing billing information for each month during the past six months.
Benefits of cloud analytics
The cloud is the future of data analytics. It’s easy to see why: cloud-based solutions are more cost-effective, scalable, and secure than traditional on-premise options. The most significant benefit of cloud analytics is that you can save time and money. Cloud-based systems involve less overhead in hardware and infrastructure, which means reduced costs.
Moreover, the cost per user decreases as your organization grows because you only pay for what you use. The scalability of cloud-based systems allows you to add more users or upgrade your plan when needed. This means you don’t have to worry about whether or not your current solution will be able to handle future growth or additional needs.
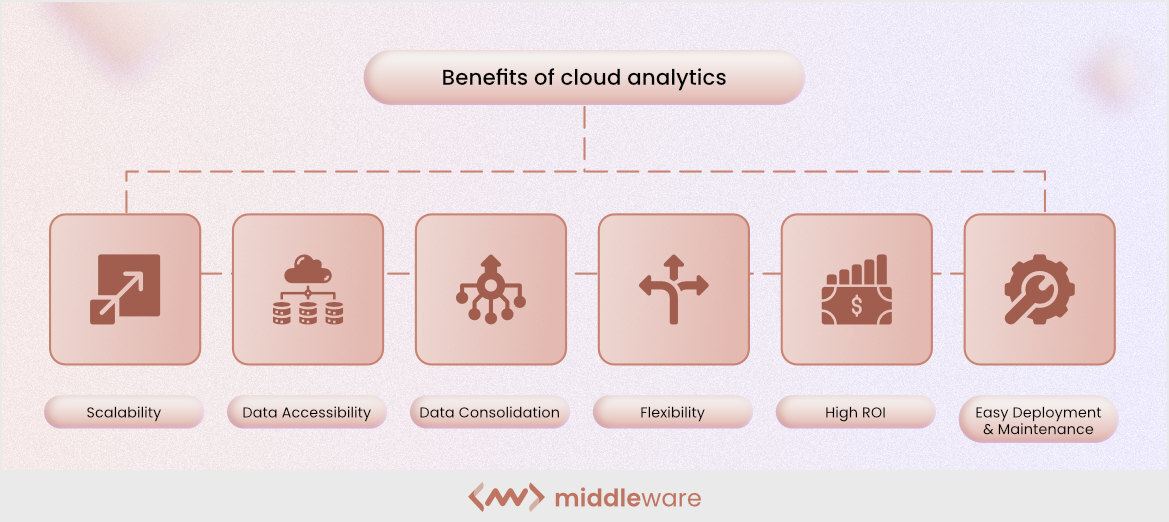
Benefits of cloud analytics:
- Scalability – Cloud-based solutions can be scaled up or down as your business grows or contracts. This gives you the flexibility that’s impossible to replicate with an on-premise solution.
- Easy Access and Collaboration – Cloud solutions offer 24/7 access via any device to get your hands on the information you need whenever it suits you. And collaborative features mean you can share data with colleagues or clients without having to worry about privacy issues.
- Flexibility – Cloud solutions are built on a pay-as-you-go basis, so there’s no need for long-term contracts or upfront payments. You only pay for what you need when you need it, making them perfect for businesses that want to keep their costs down while still benefiting from top-of-the-line technology.
- Data consolidation – Cloud solutions come with tools that allow you to consolidate data from multiple sources into one central location, which makes it easier for everyone involved in your business to understand how everything works together
- Low cost and high ROI- The cost savings from moving from on-premises software to the cloud are often significant, especially when you consider how much more efficient it is at analyzing large amounts of data.
- Easy deployment and maintenance. Cloud providers manage all aspects of operating the infrastructure required by their tools, so there’s nothing you have to do except sign up with them — which usually takes less than five minutes!
Top 3 cloud analytics tools
Cloud analytics tools are software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications that help you analyze business data. They often come with pre-built dashboards and reports, which can be customized to suit your needs.
Typically, cloud analytics tools are more affordable than on-premise solutions because they don’t require any hardware or software installation. Cloud analytics tools also offer more flexibility because they can be accessed from anywhere and from any device.
1. Microsoft Power BI
Power BI is Microsoft’s business intelligence (BI) product that helps users visualize, explore, and understand data across various platforms. It offers a wide range of features and options for business users and IT professionals alike. Users can choose from several different data visualization options, including charts, tables, and maps, depending on what kind of information they want to present or analyze. It offers a variety of features such as interactive dashboards, multiple data source integration, real-time insights, and many more.
2. Zoho Analytics
Zoho Analytics is another leading cloud analytics tool that allows users to build reports by dragging and dropping data fields into columns or rows of a table; users can also create custom charts based on their requirements using its graphical user interface (GUI). You can also create dashboards and share them with others in your organization so they can see what you’re working on and help you make decisions based on what they see in the dashboard.
3. IBM Cognos Analytics
IBM Cognos Analytics is another top cloud analytics tool developed by IBM for enterprise-level businesses that need advanced reporting capabilities. It offers everything from essential reporting tools like Excel spreadsheets to advanced analytics tools like predictive models and visualizations that give you an overview of your business at any given time. Hence, you know where it’s headed in the future and how you can make improvements accordingly.
How to choose the best cloud analytics platform?
Cloud analytics platforms are designed to allow users to process and analyze large amounts of data. They are instrumental for companies that have collected massive amounts of data through their business operations but don’t have the time or expertise to analyze it themselves. Many cloud analytics platforms use machine learning algorithms to analyze data automatically, but they also allow users to apply their own algorithms if necessary manually. The cloud platform will then run all of your algorithms on the same data set, allowing you to compare results from different models easily. When choosing a tool for your business, you should look for features like:
- Easy-to-use interface: A good cloud analytics tool should be easy to navigate and understand. That way, even if you don’t have much experience with databases or other types of data analysis software, you’ll be able to use it without issue.
- Data mining and analysis capability: Cloud analytics tools should be able to mine through large amounts of data quickly and easily. Put your supposed cloud analytics tool in action using a test database as a source and see if it can justify your data needs.
- Data visualization capability: A Cloud analytics platform should allow you to visualize your data in many different ways. Your chosen platform should be able to process structured and unstructured in a visually presentable way, such that even a non-technical person can read it.
- Your Requirements: Lastly, when it comes to choosing a cloud analytics tool, anything that matters the most (other than pricing) is ‘your specific requirements.’ Justifying your specific requirements should be the bottom line when it comes to choosing the right cloud analytics tools
Cloud analytics tools are often reserved for larger companies with extensive databases. However, even smaller businesses can benefit from cloud analytics platforms because they eliminate the need for IT personnel and other employees who might otherwise be tasked with analyzing data on their own time.
Wrapping Up
For small to medium-sized businesses, Cloud Analytics is an excellent way to keep track of your business from multiple locations. In addition to the tools mentioned in this article, there are many other options. The best way to determine which type will work best is to try a few, test them out and see which one will serve your business needs.
What is a cloud analysis?
Cloud analytics refers to storing and analyzing data on vendor-managed infrastructure to extract actionable business insights.
How does cloud analytics work?
Vital elements of cloud analytics like data sources, data models, processing applications, computing power, analytic models and sharing or storage of results are provided by a cloud service provider (CSP).
The CSP will access these resources through software application programming interfaces (APIs), allowing you to create custom software applications or use pre-built tools from the CSP’s marketplace or library.