Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides reliable, on-demand computing through a pay-as-you-go pricing model. While this brings flexibility and scalability, it also introduces demanding situations in fee management. Many businesses struggle to accurately forecast or adjust prices due to the rapid adoption of cloud services, a lack of standardization, and the complexity of AWS billing systems.
Common areas where prices spiral out of control include:
- Underutilized or idle sources: Instances and services that run 24/7 without matching real utilization.
- Lack of auto-scaling: Fixed-capability deployments that don’t adapt to site visitors’ spikes or dips.
- Incorrect storage class utilization: Storing now and again accessed information in high-priced storage tiers.
- Missed savings opportunities: Failing to take advantage of reserved instances, quantity reductions, or financial savings plans.
The freedom to control costs, while preserving the overall performance and capacity you require, is achievable through AWS’s extensive range of services and pricing options. Begin by following the 10 best practices mentioned below to help reduce your bills by 40% and immediately affect your bill, as well as help reduce your AWS prices.
Let’s understand these practices…
10 Practices to reduce AWS costs
Reducing AWS costs can seem daunting, especially if you lack the necessary expertise. Here are ten proven practices to help you cut these costs and make your business more efficient.
1. Identify Amazon EC2 instances with low CPU utilization and autoscale
Identifying low-utilized EC2 instances is a great way to reduce costs. If you provision a 16 GiB memory EC2 instance, you pay for the total capacity, not what you use. Cut down provisioning on such instances, as over-provisioned instances are one of the biggest cost drivers of AWS bills.
Use AWS Cost Explorer Resource Optimization to determine which EC2 instances are idle or underutilized. Stopping or downsizing these instances reduces high costs. You can even use the AWS Instance Scheduler to automatically stop instances or the AWS Operations Conductor to resize them automatically.
AWS Compute Optimizer also recommends downsizing instance families and instances as part of an auto-scaling group. This autoscaling feature lets you scale your DynamoDB table in and out. You can also use the on-demand option to access pay-per-request services that are less expensive and offer high performance.
With EC2 Auto-Scaling, you can launch Spot instances to meet target capacity. Spot instances can help you cut costs by up to 90% for fault-tolerant workloads like big data, CI/CD, web servers, etc. Even if your Spot instances are interrupted, autoscaling maintains the target capacity by automatically requesting more instances.
A detailed comparison of the types of instances to better understand how you can use and allocate them.
| Type | Commitment | Discount vs On-Demand | Ideal For |
| On-Demand | None | 0% | Short-term, unpredictable workloads |
| Reserved | 1–3 years | Up to 75% | Predictable, long-running workloads |
| Spot | None | Up to 90% | Cost-sensitive, fault-tolerant workloads |
| Dedicated | Optional | Varies | Compliance needs, licensing, isolation |
The EC2 Auto-Scaling group allows you to expand or shrink the EC2 fleet based on demand and review the scaling activity on the console. You can analyze the reports to see if the scaling policy can be optimized and reduced to the minimum to save costs.
A robust autoscaling solution like Middleware Auto Scaler solves this issue through predictive autoscaling that taps into AI/ML technologies to anticipate resource requirements and match them with the right capacity to run the applications at scale.
If auto-scaling is on your roadmap, our expert whitepaper will help you optimize your cloud infrastructure and save even more.
The Ultimate Guide to Auto-Scaling Your Application Infrastructure. Read Whitepaper
2. Delete unattached EBS volumes
Elastic block storage (EBS) acts as local block storage when you launch an EC2 instance. If you don’t delete these EBS volumes after terminating the instances, they will significantly change over time. AWS continues to charge you for these even if you don’t use them. This can result in thousands of unattached EBS volumes that shoot up your bill.
When you launch an instance, check the box in the AWS console to automatically delete the EBS volume when the instance terminates. This ensures you don’t pay for unattached EBS volumes, lowering overall costs.
3. Adopting Cloud Observability Platform
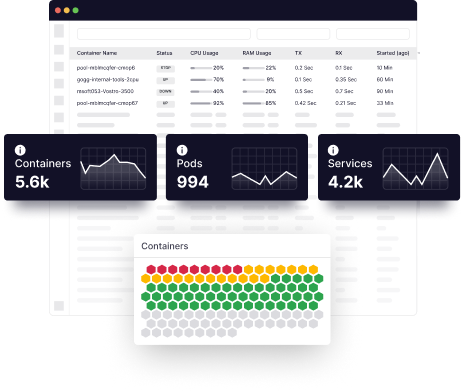
Middleware’s full-stack observability platform provides you with deeper cost visibility across all your AWS resources. It makes it simple to identify and address cost inefficiencies by automatically surfacing changes in your cloud expenses and visualizing cost data with the rest of your metrics, traces, logs, and other telemetry.
With this comprehensive insight, businesses can optimize resource allocation, eliminate unnecessary assets, and negotiate optimal pricing models, resulting in significant reductions in AWS costs. With Middleware, organizations can achieve a more efficient, cost-effective, and scalable cloud infrastructure that drives business growth and maximizes their AWS investments. Additionally, the OpsAI of Middleware will help you fix issues automatically, allowing you to focus more on creating new innovations rather than wasting time and resources.
Start monitoring your AWS application to find performance bottlenecks to save upto 40% on your next AWS bill!
For example, if an application uses more resources than it needs, it can be scaled down to reduce costs. Additionally, observability can help identify and track underutilized resources that can be turned off or scaled-down, further reducing costs.
4. Optimize container workloads using Spot and Reserved Capacity
In Amazon EKS or ECS, you can save a great deal of money by designing your cluster for the spot and reserved/on-demand types of instances. The noncritical or batch jobs will run on Spot nodes, while core workloads or system components will rely on Reserved or On-Demand nodes in order to balance reliability and cost.
Karpenter (for EKS) will also automatically provision the most cost-efficient node types and instance sizes based on pod requirements. All on their own, these features will reduce your costs dramatically, but when combined with EKS or ECS features, the cost savings is significant.
5. Move infrequently accessed data to lower cost tiers
AWS has many storage tiers. Each tier is priced differently based on the frequency of data access. Businesses often make the mistake of preferring S3 storage for all data, which can lead to higher costs.
You can cut costs by moving data that is infrequently accessed to lower tiers. This is an ideal strategy for long-term storage and data backup. Infrequent Access Storage also helps with disaster recovery, whereas with S3 Glacier, you can archive data. This way, you can minimize AWS costs without affecting efficiency.
| Need | Best S3 Option |
| Frequent access | S3 Standard |
| Unpredictable access pattern | S3 Intelligent-Tiering |
| Infrequent access with fast retrieval | S3 Standard-IA or One Zone-IA |
| Occasional archival retrieval | Glacier Instant or Flexible |
| Long-term, rarely accessed storage | Glacier Deep Archive |
6. Use reserved instances (RI)
Another excellent way to reduce AWS costs is purchasing reserved instances (RI) when possible. Cloud management platforms determine if instances are running long enough to justify purchasing reserved instances. Once you determine the need, figure out which RI type is best for you – standard or convertible. Finally, calculate the upfront costs.
Reserved instances also help reduce RDS, Redshift, ElastiCache, and Elasticsearch costs. With on-demand pricing, you get a discount of up to 42% on RIs for a year. Check purchase recommendations for better deals after adjusting parameters for one year, not upfront. The break-even point for this deal is seven to nine months, which is good in the long term.
7. Think of Architecture upgrades
Modern architecture designs, such as multi-cloud computing by using various service providers or hybrid cloud computing by leveraging both on-premise and cloud infrastructure, can help balance your cloud spending.
By partnering with different cloud vendors, such as Azure or Google Cloud, it is possible to leverage a few service-level requirements at a lower cost.
Alternatively, repairing already-existing networks, servers, and cooling, power, and supply infrastructure can reduce the price of moving applications to the cloud.
8. Right-size Your AWS Database Instances
AWS database instances can be a significant contributor to your overall AWS costs. Right-sizing your database instances involves selecting the optimal instance type and configuration to match your workload requirements.
To rightsize your database instances:
- Monitor your database performance metrics, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and I/O operations.
- Identify any overprovisioned resources, such as unused storage or excessive CPU capacity.
- Use AWS Database Migration Service (DMS) to analyze your database workload and recommend optimal instance types.
- Consider using Amazon Aurora, which provides a cost-effective and scalable database solution.
9. Implementing a Cost-Effective AWS Networking Strategy
AWS networking costs can add up quickly, especially if you have a complex network architecture. Implementing a cost-effective networking strategy involves optimizing your network design and selecting the most cost-effective networking options.
To implement a cost-effective networking strategy:
- Analyze your network traffic patterns, including data transfer volumes and network latency requirements.
- Identify any opportunities to optimize your network design, such as consolidating network resources or using AWS Direct Connect.
- Use AWS Network Cost Estimator to estimate your networking costs and identify cost-saving opportunities.
- Consider using Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) to create a secure and cost-effective network architecture.
10. Implement Amazon S3 Bucket Policies with VPC Endpoints
By implementing Amazon S3 bucket policies with VPC endpoints, businesses can control access to their S3 buckets and reduce data transfer costs. This setup allows for secure, private connectivity between S3 and EC2 instances, eliminating the need for data to traverse the public internet. As a result, businesses can reduce their data transfer costs and improve security.
Understanding AWS cost optimization tools
Cost Explorer
AWS Cost Explorer is a free service and can be accessed from the AWS Management Console. It requires no additional setup or configuration and can be used to monitor costs for multiple accounts and their linked accounts.
You can:
- View costs by service, linked accounts, tags, and more
- Identify and investigate cost drivers
- See the trend of costs over time and forecast future costs
With AWS Cost Explorer, businesses can identify opportunities to convert On-Demand Instances to Reserved Instances, modify existing RIs, or purchase new RIs to match their usage patterns. This can help businesses reduce their AWS costs by up to 75%.
AWS Budgets
AWS Budgets is a cost management tool that allows users to set custom budgets for their AWS costs and usage, and receive notifications when their costs or usage exceed those budgets.
AWS Budgets is a free service, but standard data transfer charges for Amazon SNS notifications apply if you choose to receive notifications via SNS.
AWS Pricing Calculator
The AWS Pricing Calculator is a tool that allows users to estimate the costs of using various AWS services. The tool allows users to input information about their anticipated usage of each service and provides an estimated cost.
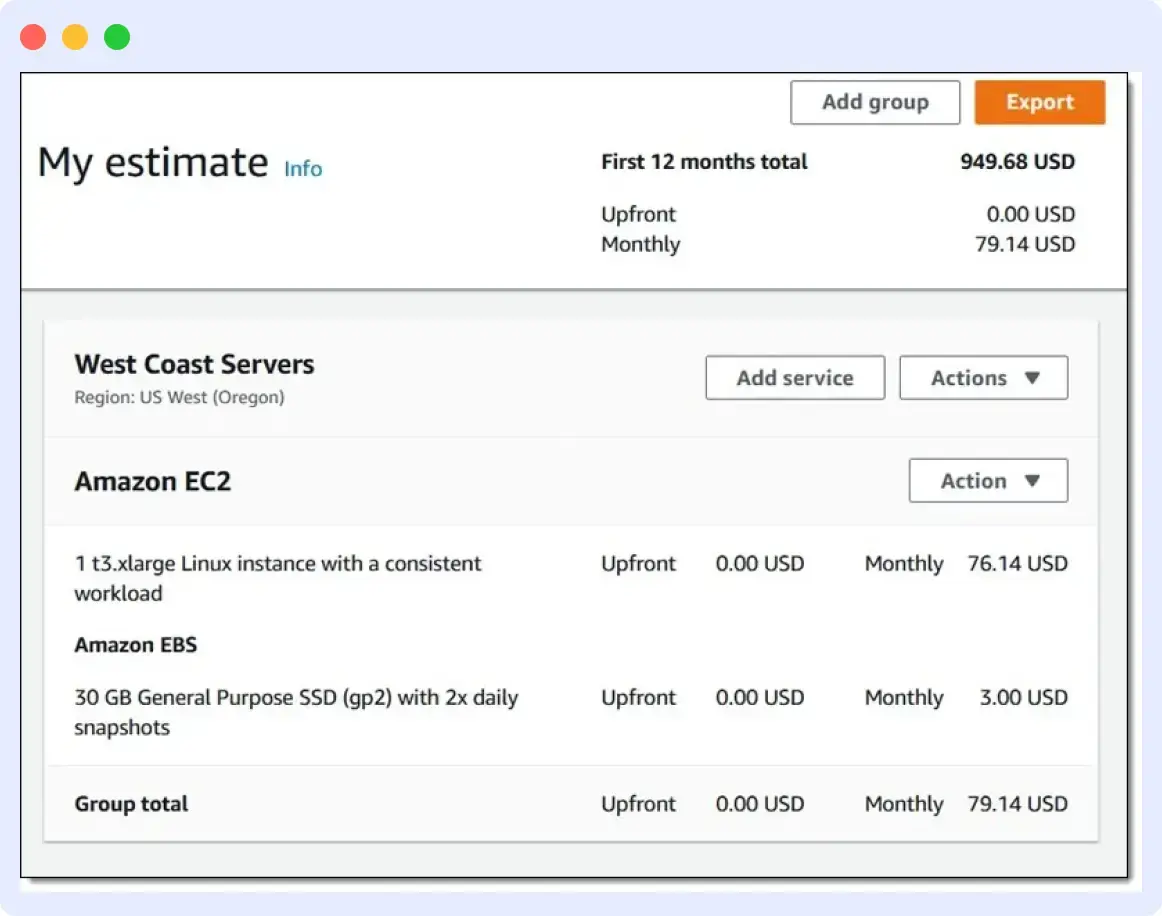
With AWS Pricing Calculator, users can:
- Estimate costs for various services including EC2, S3, RDS, Lambda, and more
- Choose between On-Demand, Reserved, and Spot instances
- Compare costs across different regions and availability zones
Sum up: Save your business from the cost trap
Small businesses often struggle with cloud costs and compromise other essential functions to keep paying these bills.
By implementing the strategies mentioned above, you can reduce AWS costs by 40% or more and ensure that business funds are used for something valuable that drives business growth and long-term success.
Middleware can help you save your AWS costs by nearly 40% using its observability solution. Request early access today to manage your cloud costs and restore transparency to the heart of cloud computing.f cloud computing.
FAQs
1. How much does AWS cost per month?
The AWS Free Tier offers 12 months of free usage for new AWS customers, with varying limits on services like S3, EC2, and Lambda. After the free tier, pricing varies depending on the services used. The AWS Pricing Calculator can help estimate costs.
2. What are the parts of AWS?
- Compute & Networking (EC2, Lambda, etc.)
- Storage (S3, EBS, etc.)
- Database (RDS, DynamoDB, etc.)
- Security, Identity & Compliance (IAM, Cognito, etc.)
- Analytics (Redshift, QuickSight, etc.)
- Application Services (API Gateway, SQS, etc.)
- Deployment & Management (CloudFormation, OpsWorks, etc.)
3. What are The Four Foundational Services of AWS?
- AWS offers to help companies reduce IT infrastructure costs.
- AWS offers security by protecting data against cyber-attacks.
- AWS offers to maintain Governmental regulatory compliance.
- AWS offers disaster recovery, mainly the amount of data lost and the length of downtime.
4. What are AWS cost optimization free tools?
- Cost Explorer
- AWS Budgets
- AWS Pricing Calculator
5. How does AWS pricing work?
AWS pricing is based on a pay-as-you-go model, where you only pay for the resources you use. Pricing varies depending on the service, region, and usage. Some services offer tiered pricing, while others charge based on usage metrics like hours, bytes, or requests.
6. What is the AWS Free Tier, and what services are included?
The AWS Free Tier provides 12 months of free usage for new AWS customers, with varying limits on services like S3, EC2, Lambda, and more. The free tier includes services like: 750 hours of EC2 usage per month, 5 GB of S3 storage per month, 1 million Lambda invocations per month, and more.