The cloud has transformed the way we do business. It has enabled companies to operate globally with the agility that wasn’t possible before. But as the use of the cloud becomes more commonplace, so do the cloud-native infrastructure challenges that come with it.
This is why we have listed 10 of the most common cloud-native infrastructure challenges in the sections below. However, since different companies face unique challenges, the list is by no means exhaustive.
Nonetheless, knowing these primary challenges is invaluable info for anyone looking to switch to cloud-native.
10 Common cloud-native infrastructure challenges
Here are the top 10 most common challenges with cloud-native infrastructure:
1. Identifying the right tools or platforms
If you’re new to cloud-native infrastructure, one of the first challenges is identifying the right tools or platforms.
As many options are available, knowing which will work best for your company can be difficult.
Fortunately, there are some tips you can follow to help you make the right decision.
First, you need to understand your company’s needs and requirements, namely:
- What are you trying to achieve?
- What are your goals?
- What kind of tool do you need to achieve your goals?
Once you clearly understand your goals, you can start researching the different options.
There are many factors to check when choosing a tool or platform; some common ones include the following:
- Cost
- Ease of use
- Features
- Support
Spend time comparing all the different options before making a final decision.
The best approach is working with an all-inclusive tool that offers cloud observability services, so you can have someone technically savvy working alongside you to help manage and monitor your infrastructure.
2. Ability to filter important metrics from the pool of metrics
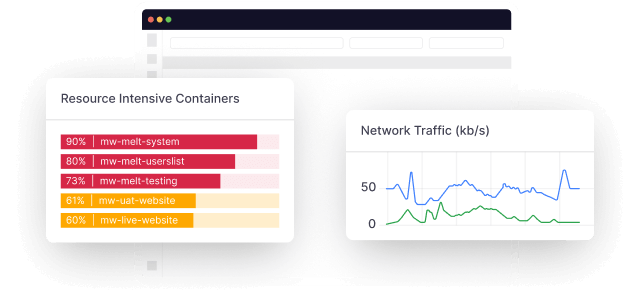
Cloud-native infrastructure generates a ton of metrics that you can easily get lost in the pile of data. Remember, your priority is to store and focus on data that matter. After all, no need to pay an abnormally high cost to store data that you don’t need.
This is where an excellent monitoring solution comes in.
A platform like Middleware allows you to customize your cloud so you can only keep the datasets you need in S3. It will help you identify and filter the important metrics, so you can focus on the ones that matter most.
This is essential in understanding your system’s health/performance and detecting any possible issues.
3. Monitoring microservices
Microservices can be difficult to monitor because they produce so much data.
The monitoring process is hectic because one microservice can run on 100 machines, and 100 microservices run on one device, and you need to track multiple metrics per service.
As such, manual monitoring may not be feasible, so you need a system that automatically tracks performance and flags issues.
That’s where a tool like Middleware comes in. We can monitor all your microservices and filter out the essential data so you can quickly identify and fix any issues.
4. Cost
Cost and confusing pricing models are other common cloud-native infrastructure challenges.
The cost of deploying and maintaining a cloud-native infrastructure can be high, especially for smaller companies that don’t have the budget to support the necessary DevOps tools or resources.
Some cloud providers offer various services to help companies save money, but those costs can add up quickly. In addition, teams may need to watch out for hidden costs associated with their cloud deployments.
For example, when spinning up a new server, teams must consider the cost of hosting and software licensing fees associated with the same. Additionally, specific tasks that require automation or specialized personnel incur additional expenses.
But partnering with the right companies can help you reduce the costs associated with maintaining a cloud-native infrastructure without sacrificing security or stability.
For example, organizations can leverage tools such as Middleware’s unified platform to monitor performance and identify potential cost-saving opportunities.
This way, you can track your spending on cloud services while ensuring that your systems are running optimally and efficiently, thereby preventing any unwanted cloud-native infrastructure challenges.
5. Security & Compliance
Security and compliance remain major challenges for cloud-native infrastructure.
As the digital world continues to evolve, new security protocols are being added, and companies must ensure their infrastructure complies with these standards.
Additionally, companies must ensure that authorized users and services have access to the data stored in their infrastructure.
One way to address these issues is to deploy a cloud observability platform that provides insights into your system’s security status and flags any anomalies ASAP.
This is because access to real-time metrics from your system can help you identify potential security threats, respond to them effectively, and remain compliant with industry regulations.
Additionally, having an observability platform that provides visibility into your cloud infrastructure can help you keep your system secure by monitoring user activity, network connections, and more.
6. Reliability issues
Reliability issues can be difficult to identify and tackle because they can stem from different elements in the infrastructure.
This makes it hard to pinpoint the root cause of errors and bugs. Remember, it may take a while before identifying the exact cause, even if you suspect it’s due to intermittent availability, sudden latency spikes, or even complete outages.
A unified platform can aggregate data across multiple sources and services so that you can quickly pinpoint problems and take preventive measures.
This will enable you to monitor the health of your cloud infrastructure and identify potential reliability issues before they become serious problems.
The best way to avoid reliability issues is to use a platform that allows easy monitoring, logging, and analyzing of the key metrics so that you can address all the problems in real-time.
7. Lack of visibility in distributed systems
The cloud is a distributed environment, which makes it difficult to gain visibility across disparate systems.
You’ll find yourself struggling to track relevant metrics, make out trends and even correlate events from various individual services.
This is because traditional monitoring tools are built on a traditional IT environment, making them inadequate for the cloud-native infrastructure.
Cloud observability services can thus provide you with a holistic view of your entire system.
A unified platform with distributed tracing capabilities can get you intelligent insights into all your microservices and enable you to identify and fix any arising performance issues proactively.
It should also have an intuitive interface to easily and accurately interpret system data.
8. Keeping up to date with outdated technologies
Keeping up to date with outdated technologies can be challenging for cloud users. To make this process easier, it’s essential to understand the technology you are using and baseline its current capabilities.
Additionally, you’ll want to utilize tools explicitly built for cloud-native infrastructure– and are under constant update and improvement.
That way, you’re sure to enjoy the latest trends in the market– and won’t ever have to worry about obsolete tools.
9. Lack of technical expertise
One of the biggest challenges for organizations transitioning to cloud-native infrastructure is the lack of adequate technical expertise.
Building and managing cloud-native infrastructure often requires people with the right skill set and experience who understand the nuances of modern application architectures and cloud platforms.
This means that companies need to develop a qualified and certified workforce to manage their cloud-native applications.
In addition, there needs to be a well-defined process for onboarding new resources, training existing personnel, and keeping an eye on market trends and emerging technologies.
To help build up these capabilities within organizations, developers should take advantage of the vast resources—blogs, tutorials, webinars, etc.—that offer insights into best practices for building cloud-native infrastructure.
Additionally, leveraging specialized vendors or service providers with experienced teams, such as Middleware, can be immensely helpful in setting up their systems for success.
10. Need for organizational shifts and team shifts
You may also discover that you must restructure your organization and teams for a successful cloud-native infrastructure. Companies often underestimate the importance of organizational changes, especially when moving to the cloud.
First, identify the roles and responsibilities that need to be added or changed when transitioning from a traditional environment to the cloud.
This can include shifting the organization’s focus from operational tasks such as server provisioning and configuration to more complex functions like automation, security compliance, and scalability.
Understanding how existing roles will change in a new cloud-native environment is also important. For example, teams used to working with physical servers may find themselves in unfamiliar territory with virtual machines or containers.
Therefore, members must acquire new skills and develop an understanding of different tools related to the cloud-native environment.
The takeaway
With so many cloud-native infrastructure challenges ahead, it’s safer to shift into cloud-native with an experienced and supportive partner.
So, what about Middleware?
Well, for one, it offers a unified cloud observability platform. This allows companies to identify, understand and fix issues across their cloud infrastructure.
Additionally, Middleware is always up-to-date with the latest technologies, so companies don’t have to worry about being left behind. It also has the technical expertise to help your team shift to a cloud-native infrastructure.