As today’s businesses increasingly rely on digital assets, such as websites and applications, to engage with customers, ensuring their performance is critical. Slow page load times, errors, and downtime can lead to lost revenue, decreased customer satisfaction, and damaged brand reputation. This is where synthetic monitoring comes in.
Synthetic monitoring is an essential tool for DevOps engineers responsible for managing application performance. By proactively identifying and addressing performance issues, DevOps teams can optimize applications, reduce downtime, and enhance the end-user experience.
So, let’s explore synthetic monitoring and how it can improve application performance.
What is Synthetic monitoring?
Synthetic monitoring is a proactive technique used to test and monitor the performance of digital assets, such as websites and applications. It involves simulating user behavior and testing from various locations to provide insights into potential issues before they affect actual users.
It is used to ensure optimal performance and user experience and can help organizations identify and address issues across the infrastructure before they impact their bottom line.
Types of Synthetic monitoring
There are several different types of synthetic monitoring, each designed to focus on specific service areas. Let’s explore some commonly used types of synthetic monitoring:
Browser-based monitoring
This type of synthetic monitoring simulates user interactions with a website or web application using a web browser. It ensures that the frameworks integrated into your website or application are compatible and function seamlessly, irrespective of the browser or operating system used by your customers.
Multiple workstations spread out throughout the globe are used in these tests to simulate user interactions and assess important performance indicators like load time, availability, and HTTP codes.
Alerts are promptly generated in the event of any problems to allow for prompt corrective action.
API and Endpoint monitoring
API and Endpoint monitoring is a type of synthetic monitoring that focuses on testing the performance and availability of APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and endpoints that support service. APIs and endpoints are critical components of modern applications, enabling them to communicate with external systems and access data.
API monitoring tools often include in-depth analytics and dashboards that let businesses monitor API usage, spot anomalies, and understand performance trends.
Additionally, these technologies assist enterprises in creating and enforcing Service Level Agreements (SLAs) with API providers and guaranteeing regulatory compliance.
Network monitoring
Network monitoring is a type of synthetic monitoring that tests the performance and availability of a service from a network perspective. It simulates transactions from various network locations to measure latency, packet loss, and other metrics.
Network monitoring tools typically simulate user transactions from different geographic locations and network providers, enabling organizations to evaluate network performance across various regions and service providers.
These tools also enable organizations to monitor network bandwidth usage, network utilization, and other key network metrics to identify bottlenecks and proactively address issues.
With Middleware’s synthetic monitoring, you can monitor the performance of APIs across multiple network levels, including HTTP, SSL, DNS, TCP, Websocket, UDP, ICMP, and gRPC.
Mobile monitoring
Mobile monitoring is a type of synthetic monitoring that focuses on testing the performance and availability of mobile applications on various mobile devices and operating systems.
It helps organizations identify issues related to mobile app performance, such as slow loading times, crashes, and errors and ensures that their mobile apps provide a seamless user experience.
Mobile monitoring tools typically provide detailed analytics and dashboards that enable organizations to track mobile app performance across different devices, operating systems, and geographies.
These tools also help organizations establish and enforce Service Level Agreements (SLAs) with mobile app developers and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Why is Synthetic monitoring important?
Synthetic monitoring allows organizations to proactively test their web applications, APIs, and other digital services by simulating user interactions.
It provides performance data from various locations and devices, helping to identify and resolve potential issues before they affect real users. This ensures a better user experience and business continuity.
- Synthetic monitoring supports A/B testing to evaluate the impact of third-party integrations on the website or application performance.
- It enables the comparison of performance in pre-production and production environments to identify potential issues before they impact users.
- Synthetic monitoring helps businesses manage externally monitored SaaS applications and ensure their performance meets service agreements.
Real-user monitoring vs. Synthetic monitoring: Distinct yet interconnected
Real User Monitoring (RUM) and Synthetic Monitoring are two distinct approaches to monitoring the performance and availability of web applications.
RUM collects data from real users’ interactions with the application, while Synthetic Monitoring generates artificial traffic to simulate user behavior. The main difference lies in the fact that RUM provides insights into user experiences, while Synthetic Monitoring can identify potential issues before users encounter them. RUM is reactive, while Synthetic Monitoring is proactive.
Nonetheless, both RUM and Synthetic Monitoring share the common goal of monitoring and enhancing the performance of digital applications, offering valuable insights into application performance and user experience.
This allows for proactive issue identification and resolution, as well as the tracking and analysis of key performance metrics like response time and error rates.
| Real-User Monitoring (RUM) | Synthetic Monitoring | |
| Pros | Provides real-time, actual user data.Offers detailed insight into user behavior. Allows for drill-down analysis to isolate issues and identify root causes. | Provides consistent and reliable testing of critical user paths and application components. Can test at scale and under different conditions. Can provide proactive monitoring. |
| Cons | Can be resource-intensive, requiring significant data storage and processing power. May not capture all user activity, particularly for users with ad-blockers or other browser extensions. Requires actual users to visit the site, limiting the ability to test under different conditions or at scale. | May not reflect actual user behavior and interactions. May not detect issues that only occur with actual user traffic, such as performance issues related to peak usage times. |
What’s the value of Synthetic monitoring?
Synthetic monitoring provides numerous advantages for organizations, enabling them to maintain peak performance, reduce downtime, and improve the user experience.
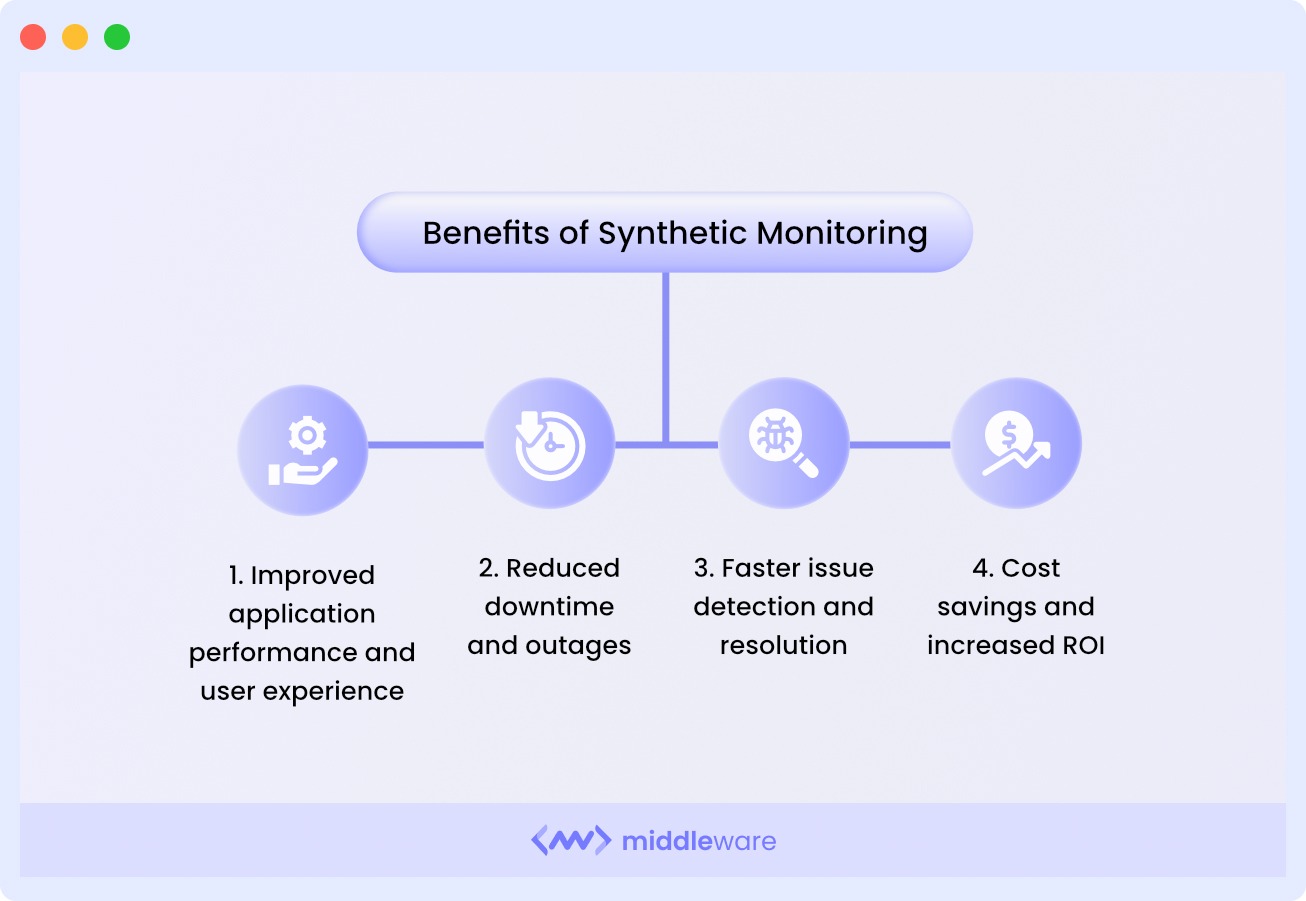
Let’s explore a few benefits of using synthetic monitoring.
Improved application performance and user experience
One of the primary benefits of synthetic monitoring is improved application performance and user experience. It helps organizations address performance issues proactively, identifying and resolving them before they impact real users.
Additionally, synthetic monitoring minimizes downtime, improves application performance, and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements.
Reduce downtime and outages
With synthetic monitoring, organizations can access detailed breakdowns of network timing data and response time by location, enabling faster root cause analysis and prompt corrective actions to minimize downtime.
Middleware allows for quick identification of performance issues with meaningful assertions and a detailed time graph, facilitating faster troubleshooting and providing a seamless user experience.
Faster issue detection and resolution
One of synthetic monitoring’s primary advantages is the expedited detection and resolution of issues. Proactively identifying and swiftly resolving problems help organizations avoid costly downtime and potential revenue loss.
Synthetic monitoring also aids in preventing reputational damage resulting from poor application performance or outages.
Furthermore, it empowers IT teams to safely test and validate changes to applications or infrastructure before implementing them in production.
This process reduces the risk of introducing new issues and enables quicker and more efficient deployment of updates and changes.
Cost savings and increased ROI
Synthetic monitoring can lead to substantial cost savings and an enhanced return on investment (ROI) for organizations.
Synthetic monitoring can reduce the need for costly emergency support and maintenance services through proactive issue identification and resolution.
It can also assist organizations in avoiding expensive downtime, which can negatively impact revenue and customer satisfaction.
Challenges in Synthetic monitoring
Implementing synthetic monitoring within an organization presents multifaceted challenges, spanning both technical and organizational realms.
Integration complexity
It’s no news that modern application development is extremely complex. Integrating synthetic monitoring into the software development lifecycle merely adds another layer of complexity.
The process must align with the ethos of Monitoring as Code, requiring automated, code-based monitoring setups. And this raises another big question within development teams: of ownership and operational responsibility.
Shared responsibility
In DevOps, the duty of building, deploying, and monitoring features falls on the same teams – that traditionally work in silos.
Synthetic monitoring demands shared ownership across development and operational domains, challenging the existing. For this to work, DevOps teams need a cohesive approach to monitoring throughout the application lifecycle.
False alert management
Synthetic monitoring, particularly with headless browsers, faces the issue of false alerts due to flaky tests. The scheduled nature of tests builds on this challenge, as unreliable results can disrupt workflows. You simply need to create robust test suites to mitigate false positives and ensure the efficacy of synthetic monitoring efforts.
Assumption validity
A fundamental challenge with synthetic monitoring lies in the validity of assumptions underlying real world scenarios. Predicting user behavior accurately proves elusive, as real users often defy expectations, engaging with applications in unforeseen ways.
To address this limitation, you can use platforms like Middleware that merge synthetic monitoring with real-user monitoring to offer a comprehensive perspective by combining synthesized usage data with insights taken from actual user interactions.
This enables informed, statistically sound analysis, bridging the gap between simulated scenarios and real-world usage patterns.
Synthetic monitoring best practices
To implement synthetic monitoring effectively, businesses need to adopt best practices that can help them achieve their goals efficiently.
These practices encompass different aspects of Synthetic Monitoring, from setting up tests to analyzing results and taking corrective actions.
Regular monitoring frequency
Monitoring too infrequently can lead to missed issues and potential downtime, while monitoring too frequently can put unnecessary strain on the system being monitored and potentially skew the results.
The ideal monitoring frequency will depend on several factors, such as the criticality of the system being monitored, the expected level of usage, and the resources available to support the monitoring activities.
However, it’s also essential to consider the impact of monitoring frequency on the system’s performance.
For example, if the system being monitored is already under heavy load, performing synthetic monitoring too frequently can exacerbate the problem and cause additional issues.
In such cases, it may be necessary to adjust the monitoring frequency to reduce the load on the system.
Comprehensive test scenarios
Comprehensive test scenarios are critical to the effectiveness of synthetic monitoring. Test scenarios should accurately reflect real-world user interactions and behavior with the system being monitored to identify potential issues that could impact end-users.
To develop comprehensive test scenarios, organizations should consider several factors, including:
- User behavior – test common user tasks and interactions.
- System components – cover all critical components, including frontend, backend, and third-party services.
- Performance metrics – measure response time, page load speed, and server uptime.
- Failure scenarios – test for server downtime, network outages, or database failures.
Realistic user behavior simulation
Realistic user behavior simulation is a critical aspect of synthetic monitoring, involving the simulation of user interactions and system behavior to identify potential issues that could affect end-users.
Consider the following key points when working on user experience:
- Define User Personas: Create personas that represent various types of users.
- Develop Use Case Scenarios: Build scenarios based on real-world usage patterns.
- Map User Journeys: Identify potential issues or bottlenecks by mapping out user journeys.
- Vary Testing Parameters: Simulate different scenarios and edge cases by adjusting testing parameters.
- Continuously Review and Update: Ensure the relevance and effectiveness of user behavior simulations through regular reviews and updates.
Configuring alerts
Setting alerts is a critical component of synthetic monitoring because it allows organizations to receive timely notifications of potential issues and take proactive measures to address them.
To set effective alerts, organizations should consider the following best practices:
- Identify critical performance metrics.
- Set alert thresholds.
- Choose appropriate alerting channels.
- Customize alerting rules.
- Test alerting mechanisms regularly.
Continuous monitoring and improvement
Continuously review and update synthetic monitoring strategies and tools to ensure their effectiveness over time.
Here are some best practices for continuous monitoring and improvement:
- Regularly review and analyze data.
- Use automated tools.
- Collaborate with relevant teams.
- Set improvement goals.
- Continuously test and optimize the system.
Top 3 Synthetic monitoring tools
Here are the top three synthetic monitoring tools:
Middleware
Middleware is a monitoring platform that specializes in complex, multi-tiered applications. It tracks the performance of web pages and APIs at various network levels and can easily deploy and scale in any environment, such as Docker and Kubernetes.
- Visualize application performance and uptime data alongside key business metrics for faster issue identification.
- Utilize a detailed time graph to identify performance issues at specific steps or endpoints.
- View a breakdown of network timing data and response times by location for quicker root cause analysis.
Click here to start using Middleware’s synthetic monitoring
Datadog
Datadog offers synthetic monitoring, enabling users to create code-free tests that simulate user transactions on applications and monitor key network endpoints across different system layers.
- Proactively monitor your endpoints through API tests to stay ahead of potential issues.
- Capture critical transactions without coding using our fully hosted web recorder.
- Ensure secure monitoring of any environment by utilizing your own private locations.
New Relic
New Relic is a cloud-based observability platform that provides real-time monitoring of software applications, infrastructure, and customer experiences.
- Detects low-performing entities like URLs, APIs, and services proactively.
- Collaborate to resolve issues automatically generated from affected tests.
- Leverage alerts and AI to seamlessly transition from synthetic checks to automatically generated tickets within AIOps.
How do you choose the right Synthetic monitoring method?
To select the appropriate monitoring method for your requirements, consider several factors, including:
- The types of applications or services you are monitoring (e.g., web applications, mobile apps, APIs, or microservices).
- The criticality of your services and the potential impact of downtime or performance issues.
- The target audience of your services (e.g., internal employees, external customers, or partners).
- The level of visibility and granularity required for monitoring (e.g., transaction traces, code-level visibility, or network performance).
- The cost and resources needed for implementing and maintaining the monitoring solution.
- The level of automation and integration required for monitoring (e.g., integration with other tools or platforms).
- The expertise and experience needed for managing and interpreting monitoring data.
- The compliance and regulatory requirements your organization must meet.
Final thoughts on Synthetic monitoring
Synthetic monitoring is essential for organizations aiming to ensure optimal performance and availability of their applications and services.
By implementing best practices and choosing the right synthetic monitoring tool (like Middleware), organizations can proactively detect issues, optimize systems, and enhance the end-user experience, leading to increased revenue and improved customer satisfaction.
Take the next step. Try Middleware for free.