Having a robust cloud strategy is really important in today’s cloud-first world, where according to Right Scale’s report, 94% of enterprises are running on the cloud.
The cloud is a dynamic place that changes almost as often as the weather. So it’s difficult to keep up with all the new features and product updates, let alone figure out which ones are right for your business.
Therefore, developing an effective cloud strategy is essential to avoid getting caught up in a whirlwind of technological distractions (and a hefty monthly bill).
In this blog post, we’ll walk you through the basics of cloud strategy and dive into ways to get started with a cloud strategy roadmap so you can easily design one for your business.
What is a cloud strategy?
A cloud strategy is a plan that outlines the best practices, tools, and services to use when implementing a cloud solution. It’s a vital tool for businesses looking to optimize their cloud adoption, implementation, and operations. A cloud strategy can be applied to most, if not all, types of cloud deployments. This includes public, private, hybrid, and multi-cloud strategies.
The six guiding cloud strategy principles of adopting and using the cloud are trust, enablement, enterprise risk, capability, cost-benefit and accountability.
Having a cloud strategy in place guides your cloud journey. This is especially important given that businesses of all sizes have varying requirements when it comes to cloud solutions. A cloud strategy gives you a clear path to leverage the benefits of cloud computing while helping you avoid costly mistakes and pitfalls along the way.
Companies like Deloitte and Mc Kinsey offer to help clients navigate the end-to-end journey from on-premises to cloud and see the transformational capabilities of the cloud for business enablement and competitive advantage.
Why do you need a cloud strategy?
With increasing cloud adoption, organizations are now looking for a cloud strategy to maximize their benefits. It’s a critical component of any organization’s IT strategy today. With the increasing adoption of AI, data science, and machine learning, organizations are extending native technologies to their clouds to create and deploy scalable applications in modern hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Cloud-native strategy has many benefits for organizations. It’s a comprehensive plan that ensures successful cloud adoption and operation at scale. A well-thought-out cloud native strategy saves costs, meets critical business milestones, and achieves your digital transformation objectives in a diverse cloud setup.
Organizations that don’t consider the best practices, tools, and services required to build a cloud-native strategy risk driving up their costs and negatively impacting their customers. Here are a few reasons why you need a cloud-native strategy.
Become agile and save costs
Cloud-based solutions enable companies to scale resources up or down as needed, which is essential for ensuring that organizations can keep pace with their workloads and customers’ ever-increasing expectations. But it’s not just about speed – it’s also about cost.
Cloud solutions often reduce IT budgets while freeing internal resources to focus on high-value activities. This, in turn, leads to higher employee productivity, happier customers, and a lower rate of attrition among experienced IT professionals.
Align your vision and objectives
A cloud native strategy supports your goals and objectives – what you aim to achieve through your cloud adoption journey. It also aligns with your culture and overall vision. This helps you understand how you see yourself in the future and how different cloud environments can play a role in helping you reach your desired future state.
Select the right cloud platform(s)
One of the first considerations to make as part of your cloud-native strategy is choosing the right cloud platform. Understanding business needs and goals help you find the best cloud solution.
With a clear strategy, you can easily estimate:
- Cloud costs, including acquisition costs and ongoing operational costs
- The security features you expect from a solution
- Scalability your cloud solution should offer
- Compliance and regulatory requirements it should meet
- Specific customer needs based on the industries you serve
Identify your cloud implementation plan
A cloud strategy roadmap is a plan that outlines the key steps and activities you’ll follow when implementing a cloud solution. It helps you understand the various activities involved in the cloud implementation process and provides a path to help you reach your desired outcomes.
Your cloud strategy includes this implementation roadmap and provides more information on:
- The current state of operations: What is your current state of operations? What challenges or bottlenecks do you face? What resources are currently being used?
- Cloud adoption strategy: How should your cloud adoption strategy align with the current state of operations? What should your cloud adoption strategy look like based on your goals and objectives?
- Cloud implementation roadmap: How should your cloud implementation roadmap align with the existing state of operations? What should your cloud implementation roadmap look like based on your cloud adoption strategy?
A cloud strategy plays a vital role in cloud adoption and migration, enabling organizations across industries to streamline processes, increase collaboration, and cut costs.
How to get started with a cloud strategy roadmap?
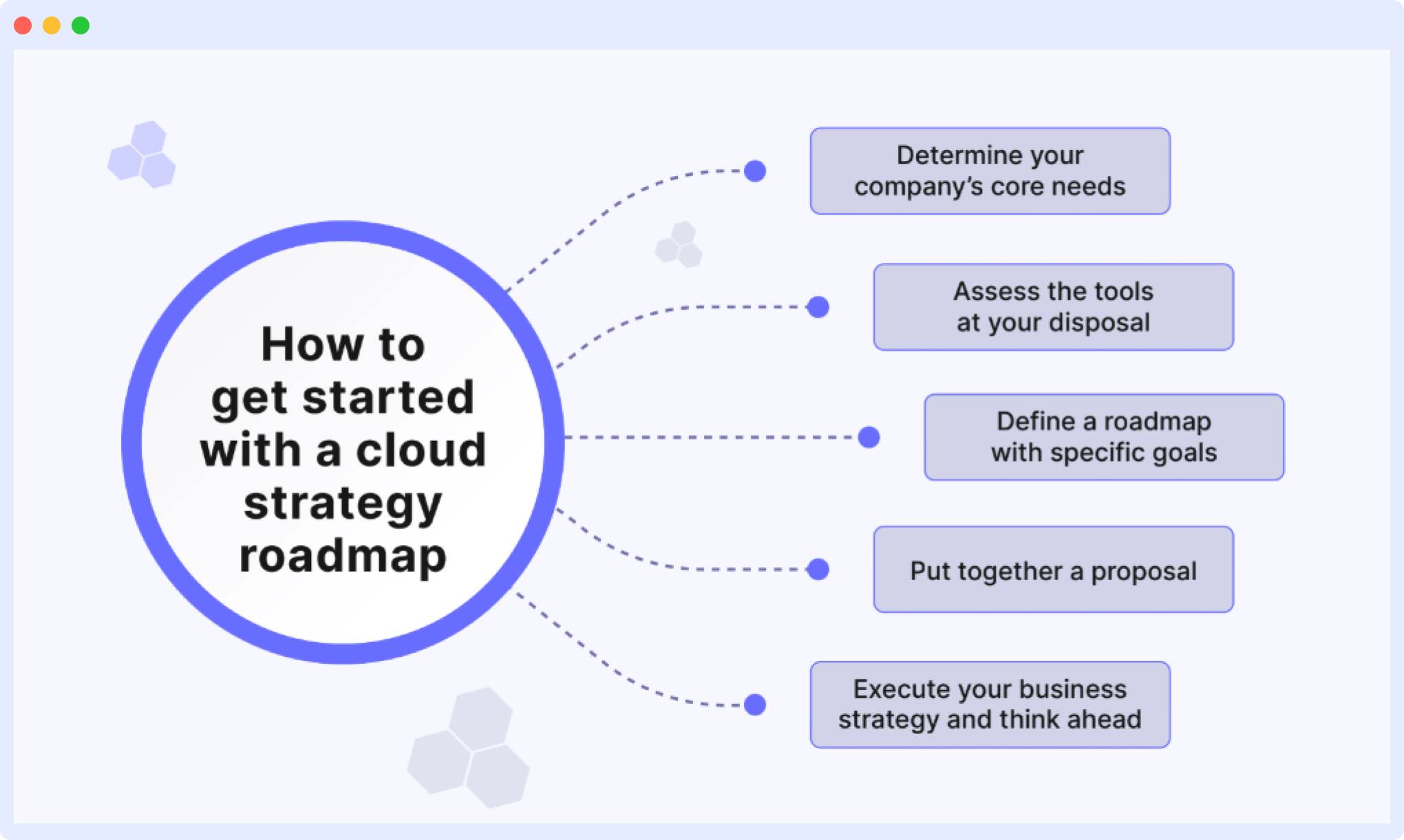
Getting started with a cloud strategy roadmap can be a bit complex. Here’s a simple five-step checklist to ease some of the complexities and challenges involved in creating a roadmap.
Determine your company’s core needs
You can’t select the right service until you understand your company’s needs. The following questions can help guide you as you put together a shortlist of services that match your requirements:
- What are our core values and purpose?
- How will we use the service?
- What are our key metrics and KPIs?
- What are our customer expectations?
Suppose you’re in healthcare and need robust data-security protocols to comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) regulations. In that case, you might rule out most public cloud providers. A private cloud infrastructure (or a hybrid cloud approach) is a more appropriate solution.
Assess the tools at your disposal
Assessing the tools you currently use in the cloud is just as important as determining your core needs. This is because your current services will either help or hinder your efforts to reach new goals.
You can use cloud inventory tools to get a holistic view of your current cloud services. With these tools, you can take a snapshot of your existing cloud services and compare it with a shortlist of new services you’re considering.
What’s more?
You get a side-by-side analysis of what each service can do and its associated cost. Furthermore, a clear picture of your current services’ use helps determine if they’re compatible with new cloud offerings.
Define a roadmap with specific goals
Before shopping for new services, you should have a roadmap with specific goals. Let’s say you want to expand your global reach but are unsure where to start. You might decide to adopt an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) solution like Amazon Web Services (AWS).
With AWS, you can quickly scale up your infrastructure in the regions where your customers are located. You can also use the AWS Marketplace to find third-party services that provide localization, compliance, and cybersecurity services to meet your regulatory requirements.
Put together a proposal
Okay, so you’ve identified your needs, assessed the existing tools at your disposal, and have a roadmap with specific goals in mind. Now it’s time to put together a proposal for new services.
We recommend using a spreadsheet to create a table comparing your current services with the new ones you’d like to adopt.
The table should have five columns.
- The current services
- The new services
- Reason for the change
- What changes the way we use the services
- Stakeholders responsible for each service
Let’s say you’re considering a managed file transfer service to replace a manual process that’s currently bogging down your operations team. Include how long the process takes, how many people it impacts, and what changes about the process if you adopt the new service.
You should also include who’s responsible for implementing and maintaining the current and new processes.
Execute your business strategy and think ahead
Now that you’ve completed the five essential components of a cloud-computing strategy, it’s time to put your plan into action. It’s important to keep in mind that this is a fluid process.
When you adopt a new cloud architecture, you should start thinking about the next business outcomes. The cloud is a dynamic landscape; to stay ahead in the game, you need to be nimble and open to change.
What are the benefits of a cloud strategy?
A cloud strategy allows a company to take advantage of cloud-based services without sacrificing security or control. It gives you a clear roadmap for how and when to adopt different services, helps keep pace with changing cloud technology, and minimizes risks.
If you’re struggling to decide whether the cloud is right for you, here are some benefits of using a cloud-first approach as part of an overall cloud adoption or migration plan.
It’s the perfect guide
Cloud adoption is not one-size-fits-all. Understanding how different parts of your business can benefit from specific cloud services is essential. A cloud strategy lays the foundation for how you can take advantage of specific cloud services based on your use cases. It also guides you on how to prioritize cloud investments and whether to invest in a managed service provider (MSP) for extra support.
A clear strategy can also help you understand if you need an internal IT staff dedicated to running cloud-based infrastructure, which cloud services you can use right now, and services you can implement in the future as you grow.
Helps you stay safe and secure
To take advantage of the benefits of the cloud, you need a safe and secure environment while using new technology. A cloud strategy can help you identify ways to mitigate the most common risks associated with cloud computing.
The biggest risk associated with cloud adoption is the loss of control of data. An organization’s data is often distributed across the cloud. This can raise the question of who has access to the data. Because the cloud has inherent security risks, organizations must be diligent about protecting their data. You can take many initiatives to minimize these risks and maintain a high level of security.
Provides a clear roadmap for future tech investments
As your organization grows, you must invest more in different technologies to keep up with the demand. A cloud strategy can help you forecast these tech investments in infrastructure, security, and operations.
You can also forecast how much your infrastructure, security, and operations costs will increase over time. Cloud service providers charge for services like storage, computing power, and bandwidth. To forecast your future costs, you can determine how much you need to spend on these services.
Enables you to take advantage of changing technology
A cloud strategy allows you to adopt specific cloud services based on your company’s needs. You also have the flexibility to change services as your business evolves. A well-designed cloud strategy lets you understand which services to implement now and save for the future. Modernization in your tech stack and application development initiatives enables your DevOps to make use of the right tools and automation to deliver even more business value.
How does a cloud strategy roadmap work?
Building a cloud strategy roadmap is a great way to visualize the process you’ll follow to build your cloud solution. The roadmap can include key milestones, like when you plan to start interviewing potential vendors and information about each stage in the process.
Be sure to include the total cost of ownership and other relevant information like your team’s skill set and your current IT budget size. Your roadmap can help you stay on track and communicate your progress to senior leadership. Finally, make sure you share your roadmap with your team. Not only will this help keep everyone informed, but it will also give your team a sense of ownership over the project.
What are the challenges of a cloud strategy?
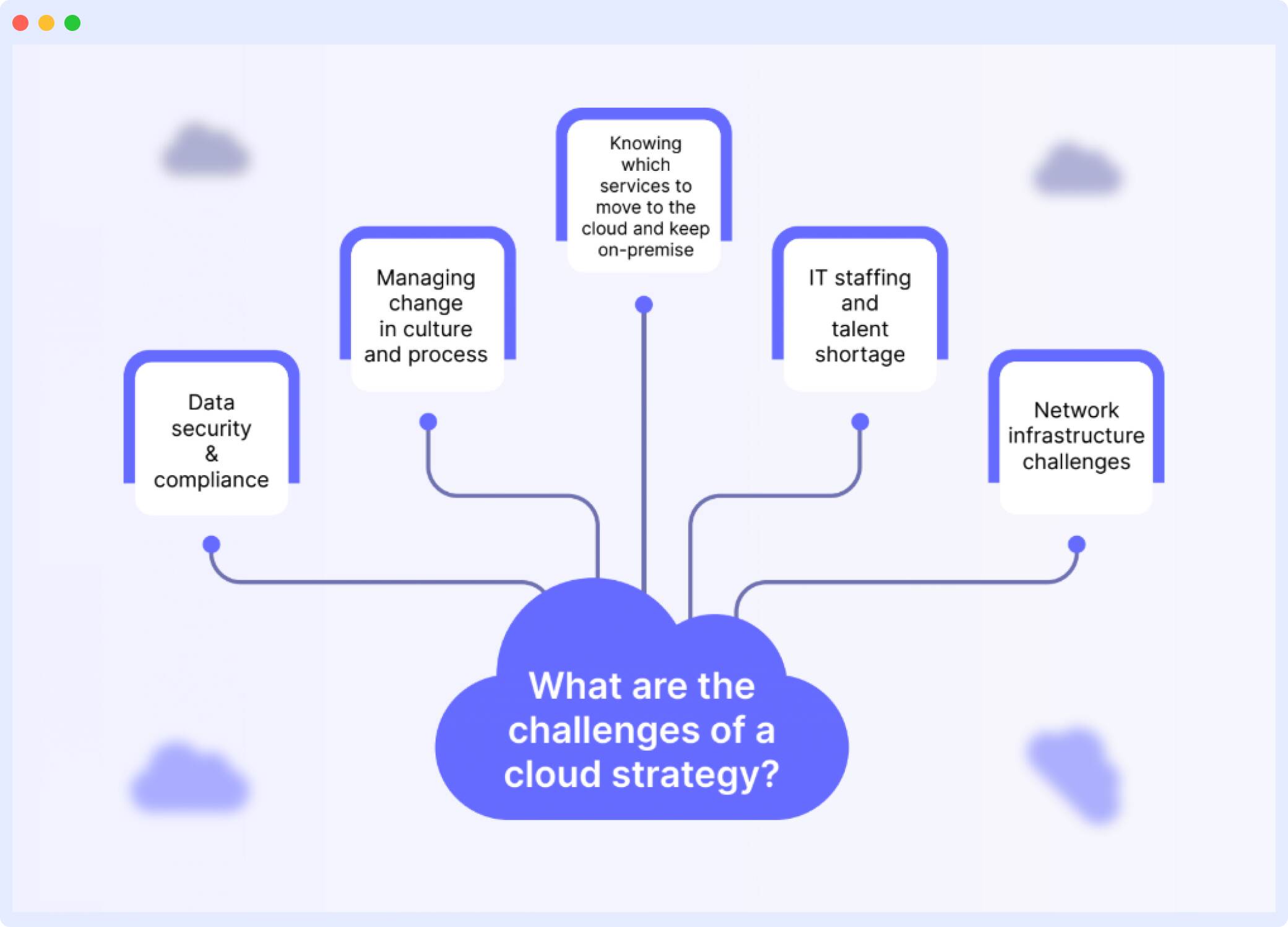
Cloud is not just a trend; it’s an ongoing and inevitable shift in how enterprises adopt and deploy technology to meet their business goals. Cloud services have become the de facto standard for nearly all businesses, from startups to established enterprises looking to optimize their IT infrastructure, lower operational costs, and increase agility.
However, for most organizations, moving to the cloud is not as simple as adopting a standard or private cloud deployment model.
Every organization must consider various factors and challenges with cloud migration.
Data security and compliance
Any move to the cloud will be a compliance risk, no matter how careful you are. More than just the risk of data being hacked, the risk is more around what happens if the company hosting your data goes out of business or gets acquired by another business with different data security standards.
For example, if you store your data with Amazon or another commercial cloud vendor, you need to set a different set of security and compliance controls compared to what you’re used to if you’re hosting that data on-premises. This necessitates having controls such as Hardware Security Module (HSM) based key management, encryption, and policies that follow strict government standards such as SOC 2, PCI, and HIPAA.
Managing change in culture and process
One of the biggest challenges with moving to the cloud is changing the culture around IT. As part of this change, you need to be agile and shift and pivot on demand as business needs change. The days of mapping out every project to the finest detail and defining project timelines that extend over months or even years are over.
In the cloud, changes to project timelines are the norm. For example, when building out your new application in a public cloud environment, you can’t assume you will have the same number of servers simultaneously each day. Quickly responding to demand changes and adapting your application to these changes is a must. You should be able to spin up new resources and shut them down just as quickly.
Knowing which services to move to the cloud and keep on-premise
Not all services and applications should be hosted in the cloud. When migrating applications to the cloud, it’s important to ask yourself questions to help you make the right decision for each application.
- Do you have a consistent or unpredictable demand for the application? Hosting the app in the cloud makes sense if the app demand is unpredictable. If predictable, it may be best to keep it on-premises.
- Does the application need to be accessed when the business hours are? If your app needs consistent access, hosting it in the cloud may not be the best option.
- Do you have the data that must be on-premises to support the application? When you have the right data, you can offload that data to the cloud and keep the application on-premises.
IT staffing and talent shortage
If you’re struggling to attract and retain top IT talent, moving your IT operations to the cloud may not be the best decision. Moving to the cloud requires your IT team to learn new skills and have a different level of expertise.
If your team is already stretched thin and doesn’t have the bandwidth to take on the challenge of moving to the cloud, you may want to consider waiting until it has more capacity to take on the additional work. By waiting until your team can transition to the cloud, you can take advantage of the economies of scale that come with hosted services and products.
Network infrastructure challenges
Depending on how you architect your network, transitioning to the cloud may require you to make significant changes. You may need to upgrade your network hardware and software to support the additional demand that comes with supporting cloud services.
If you have an old network architecture, it may not support the new demands of cloud services. In these cases, you may invest significantly in new hardware, software, and other resources to accommodate new cloud services. If you don’t make these changes before moving your services to the cloud, your new hosted services may run into capacity issues.
2 key things to remember for cloud strategy framework
If you want to transition to the cloud, you’re not alone. In fact, it’s become a common challenge for organizations of all sizes.
First, consider if you need to make a move, and second, keep cost in mind.
Middleware is built to deliver just the right insight you need. With Middleware’s observability platform, you can operate confidently while keeping track of your costs.
To learn more about how Middleware can help you measure, monitor, and optimize your cloud spend — Request a demo today.
FAQs
What is a Cloud strategy framework?
The phrase “cloud computing Framework” is a broad term. It lists all the tools and technical expertise needed to design, manage, and maintain cloud applications.
Explain Cloud strategy with an example?
It took 7 years for Netflix to transform its application and adopt microservices to move to AWS. End result was that compared to on-premise resource management, the restructured application structure increased service availability and decreased IT expenses.
What are Cloud Deployment models?
There are three main types of cloud deployment models: public, private, and hybrid.
- Public Cloud: Owned and operated by a third-party provider and made available to the public over the internet. You only pay for the resources you use.
- Private Cloud: Owned and operated by the company, and only authorized users within the organization to have access to them.
- Hybrid Cloud: Combines elements of both public and private clouds, allowing organizations to take advantage of the cost savings and scalability of public clouds.
What are 3 main cloud Delivery models?
- Host: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) Example: Amazon Web Services (AWS)
It delivers computing infrastructure as on-demand services. User purchases servers, network equipment, software data center space, and rent those resources
- Build: Platform as a Service (PaaS) Example: SAP Cloud
It allows developers to build applications and services on the internet and the deployment models include public, private and hybrid.
- Consume: Software as a Service (SaaS) Example: Hubspot
It is a software delivery model where cloud provider
What is a cloud-first strategy?
It means you take advantage of the economies of scale offered by cloud hosting providers like Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, Amazon AWS, etc. Your developers build, deploy, and can more readily scale to meet the ever-growing demand placed on your company.
A Cloud-First Strategy ensures:
- Observability
- Configurability
- Lower costs
- Scalability
- Reproducibility
- Reliability