Data teams today manage data from many sources and are expected to deliver insights faster than ever. With inputs coming from SaaS tools, product events, marketing platforms, and internal systems, keeping transformations consistent, documented, and reliable becomes increasingly difficult as pipelines grow.
Most modern organizations now rely on cloud data warehouses such as Snowflake, BigQuery, Redshift, and Databricks. This shift has moved data transformation inside the warehouse, following the ELT approach, loading raw data first and transforming it later. While ELT improves scalability, it also introduces challenges like version control, data quality validation, documentation, and dependency management.
This is where data build tools come in. A data build tool provides a structured way to transform raw warehouse data into analytics-ready datasets. Among these tools, dbt (data build tool) has emerged as the industry standard, enabling teams to build, test, and maintain reliable data models without managing complex infrastructure.
👉 Data transformation is only one piece of the reliability puzzle. Learn how top teams use database monitoring software to catch issues before dashboards break.
What is a Data Build Tool?
A data build tool helps teams transform, test, and manage data inside a data warehouse. Instead of using scattered SQL scripts, these tools bring better structure to analytics work, like modular code, version control, automated testing, and clear dependencies.
In a modern data stack, data build tools work after data is loaded and before it’s used for reports. They don’t need complex infrastructure to turn raw data into clean, ready-to-use datasets.
The most popular tool in this group is dbt (data build tool). It uses SQL to transform data and enables analysts to build data models in the same way developers write code. This makes transformations clearer, easier to document, and more consistent.
How Data Build Tools Fit Into the Modern Data Stack
In a modern data stack, data build tools sit between raw data ingestion and business intelligence tools. They do not collect data from external sources. Instead, they operate directly inside the data warehouse.
For example, tools like Fivetran or Airbyte load raw tables into the warehouse. A data build tool then transforms the raw tables into clean, business-ready models, including customer, order, revenue, and retention metrics. These transformed models are what dashboards and analytics teams rely on.
By keeping transformation logic centralized, data build tools ensure that every analyst, dashboard, and stakeholder works from the same definitions, eliminating inconsistent metrics across teams.
What dbt Is Not
It’s important to know what dbt doesn’t do:
- Not an orchestration tool: dbt doesn’t schedule jobs. You need tools like Airflow or Prefect for that. Orchestration tools manage when jobs run. dbt focuses only on how data is transformed once it already exists in the warehouse.
- Not an ingestion tool: dbt doesn’t pull data from sources into your warehouse. It only transforms data that’s already there. Data ingestion tools handle extraction and loading. dbt intentionally avoids this responsibility to remain lightweight and warehouse-native.
dbt does one thing well: it turns raw data into trusted, structured datasets through clean, testable transformations.
ETL vs ELT: Why Data Build Tools Exist
Traditional data pipelines followed the ETL model: extract data, transform it using external systems, then load it into a database. This approach worked when data warehouses had limited compute power.
Modern cloud warehouses changed this model. With scalable compute and storage, transformations can now run directly inside the warehouse.
This shift created the ELT approach: extract, load, then transform. However, ELT requires a reliable transformation framework. Writing ad-hoc SQL scripts quickly becomes unmanageable as pipelines grow.
Data build tools like dbt were designed specifically for ELT pipelines. They provide testing, documentation, dependency management, and version control all directly inside the warehouse.
What Are the Benefits of Using dbt?
dbt makes data transformation easier by bringing software engineering practices into SQL work. Here are some of the core benefits:
- SQL-first development
You can use dbt if you know SQL because it allows you work directly with SQL. No other programming languages required.
- Version Control & Collaboration
dbt uses Git to track changes. You can see what changed, who changed it, and undo mistakes. Multiple people can work together without conflicts. This allows analytics engineers to review changes through pull requests, similar to application development workflows.
- Automated Documentation
dbt automatically creates documentation for your data models. It shows table structures, column descriptions, and how datasets connect to each other, all without manual work.
- Built-In Data Testing
You can create tests to verify that values are not null and that IDs are unique, ensuring the data is accurate. dbt runs these tests each time your transformations execute. Errors are therefore detected early.
For example, if a revenue model accidentally produces duplicate records, dbt tests can stop incorrect numbers from reaching dashboards used by leadership.
- Modular & Reusable Transformations
Write your transformation logic once and reuse it across multiple analyses. You only need to alter it in one place for it to take effect everywhere that model is used.
- Fast Development and Deployment
dbt compiles your SQL, runs transformations in your warehouse, and automatically handles dependencies. This speeds up how quickly you can build and update data pipelines.
📊 Beyond tests in dbt, preventing data pipeline failures requires proactive monitoring at the database level. Discover top ways to prevent database failures and improve pipeline resilience.
How Does dbt Work?
dbt transforms SQL files, tests, and setups into dependable warehouse data models. All pipelines are coded, stored in a project folder, and executed with simple commands.
dbt Architecture
When you run dbt, it does not execute SQL immediately. dbt first compiles all models, resolves dependencies, and builds a directed acyclic graph (DAG) that determines execution order.
dbt compiles all models, builds a dependency graph, and then executes transformations inside the data warehouse based on those dependencies. During execution, dbt applies materializations, runs data quality tests, and generates documentation all from a single, version-controlled project structure.
📘 Learn how Middleware integrates with databases like PostgreSQL, MySQL, Snowflake, BigQuery, and more. Explore Middleware database integrations →
1. Models: Your Transformation Logic
Models are SQL files that transform your data. Each model contains a SELECT statement that transforms raw data into something useful. Here’s what a typical model looks like:
SELECT customer_id, COUNT(order_id) as total_orders, SUM(order_amount) as lifetime_value FROM {{ ref(‘orders’) }} GROUP BY customer_idThe {{ ref(‘orders’) }} syntax tells dbt that this model depends on another model called “orders.” dbt determines the correct sequence and runs these models in the correct order, storing the results as tables or views in your data warehouse.
💡 Discover how Middleware provides real-time insights into APM, traces, logs, and database metrics in one place. Explore Middleware’s observability capabilities →
2. Sources: Connecting to Raw Data
Sources tell dbt where your raw data lives. Instead of hardcoding table names like raw_database.orders everywhere, define them once as sources. Your project becomes cleaner and easier to edit. If your raw data changes schema, you change it once instead of in dozens of files.
3. Tests: Catching Problems Early
Tests check that your data looks right. You can check that “this customer_id column should never be null” and “every order_id should be unique.” dbt performs these tests automatically and displays the failing test in the command line so you can fix it instantly.
4. Documentation: Keeping Everyone on the Same Page
dbt generates documentation from your project automatically. It builds a webpage with all your models, their connections, and column meanings. The documentation contains a lineage graph showing data flow from sources to transformation models.
5. Materializations: How Results Get Stored
Materialization is just a fancy word for “how should dbt save this model?” You have different options:
- Table: rebuilds the entire table each time (good for smaller datasets)
- View: Creates a virtual table that runs the query when accessed (saves storage but is slower)
- Incremental: Only processes new or changed data (efficient for large datasets)
- Ephemeral: Doesn’t save anything. Just uses the logic in other models (saves space)
You pick the right materialization based on data size and how often it changes.
Getting Started with dbt
dbt is easy to use for non-data engineers. After installing, what you’ll be doing is writing code, running commands, and seeing results.
This example uses dbt Core with DuckDB, which is ideal for beginners because it requires no cloud setup and works locally.
Installation
First of all, you have to choose the versions of dbt you want to work with:
dbt Core (What we’ll use)
- Free and open source
- Runs on your computer via command line
- You manage everything locally
- Best for learning and smaller projects
dbt Cloud
- Web-based interface (no command line needed)
- Includes a built-in code editor and scheduler
- Free tier available, paid plans for teams
- Best for teams who want a managed solution
What you’ll need:
Before installing dbt Core, you need:
- Python (dbt runs on Python)
- Data warehouse
Note: The command might be different for Windows users because I’m using macOS. But the steps are the same.
If you are new to dbt, this walkthrough helps you understand the full workflow from raw data to transformed analytics models.
Step 1: Install Python
Check if Python is already installed. Open Terminal, then type:
python3 --versionIf you don’t see the version, then install Python:
brew install python3Step 2: Install dbt Core with DuckDB
Before 1.8, installing an adapter automatically installed two things:
- The adapter (dbt-duckdb, dbt-postgres, etc.)
- dbt-core (main engine)
Adapters are now installed without dbt-core. You must install both when installing dbt now:
Wait for the installation to complete, then verify it worked:
Step 3: Start the dbt Project
Create a folder and move into it:
Initialize a new dbt project:
Since you used DuckDB, enter 1.
Go to your project folder:
You should see these folders:
- models/ – Where your SQL transformation files go
- tests/ – For data quality tests
Step 4: Create Sample Data
Create raw_orders.csv in the seeds folder and add following content:
order_id,customer_id,order_date,order_amount
1,101,2024-01-15,250.00
2,102,2024-01-16,175.50
3,101,2024-01-17,300.00
4,103,2024-01-18,450.00
5,102,2024-01-19,125.00These are fake customer orders.
Load this data into your database:
Step 5: Write Your Model
Create a file (customer_summary.sql) in model/example folder and add this:
SELECT
customer_id,
COUNT(order_id) as total_orders,
SUM(order_amount) as total_spent,
AVG(order_amount) as average_order_value,
MAX(order_date) as last_order_date
FROM {{ ref('raw_orders') }}
GROUP BY customer_id
What’s happening here?
- {{ ref(‘raw_orders’) }} tells dbt to use the raw_orders data we loaded
- You’re counting orders, summing amounts, and finding averages per customer
Step 6: Run your transformation
Now execute the transformation. Run this:
dbt will run your SQL and add a new table called customer_summary in your database.
Step 7: Check Your Results
Verify the transformation worked. Install DuckDB CLI to query your database:
Edit the path in profile.yml to have this:
my_first_project:
outputs:
dev:
type: duckdb
path: ./my_first_project.duckdb
schema: main
threads: 1
prod:
type: duckdb
path: prod.duckdb
threads: 4
target: dev
Open your database:
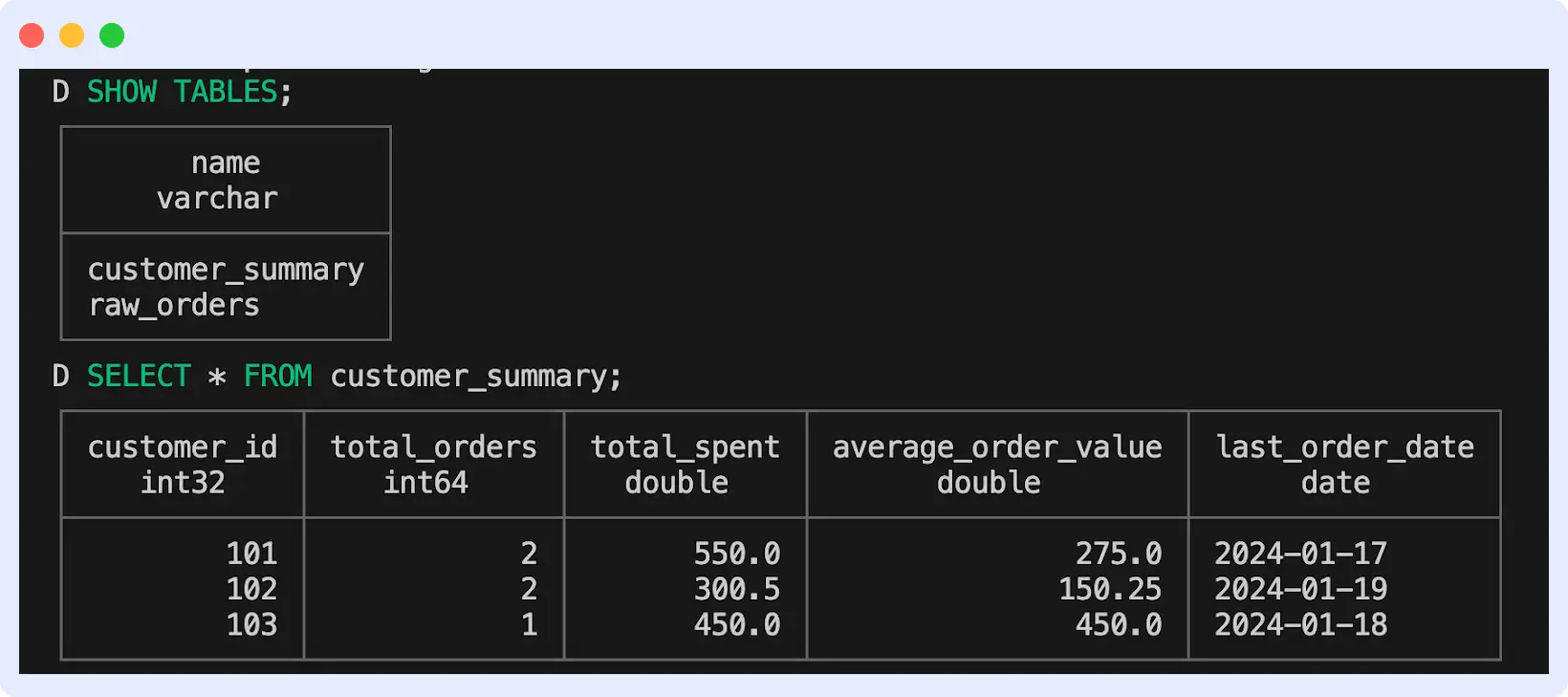
Check the list of tables with SHOW TABLES; and query your new table with SELECT * FROM customer_summary;
You should see this:
Step 8: Add a Test
In your models/example/schema.yml file, a test should already be configured. If not, create the file and add this:
version: 2
models:
- name: customer_summary
description: "Summary of customer order behavior"
columns:
- name: customer_id
description: "Unique customer identifier"
data_tests:
- unique
- not_null
- name: my_second_dbt_model
description: "A starter dbt model"
columns:
- name: total_spent
description: "Total amount spent by customer"
data_tests:
- not_null
This will make sure customer_id is always unique (no duplicates).
Run the tests:
All tests should pass. If someone accidentally creates duplicate customer records, dbt will catch it.
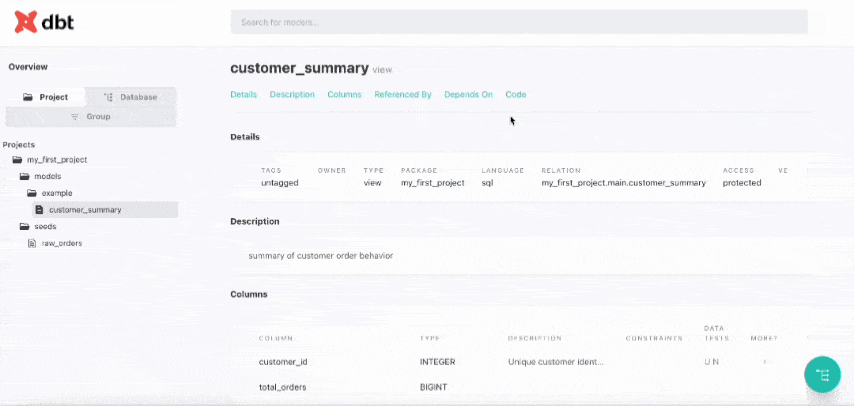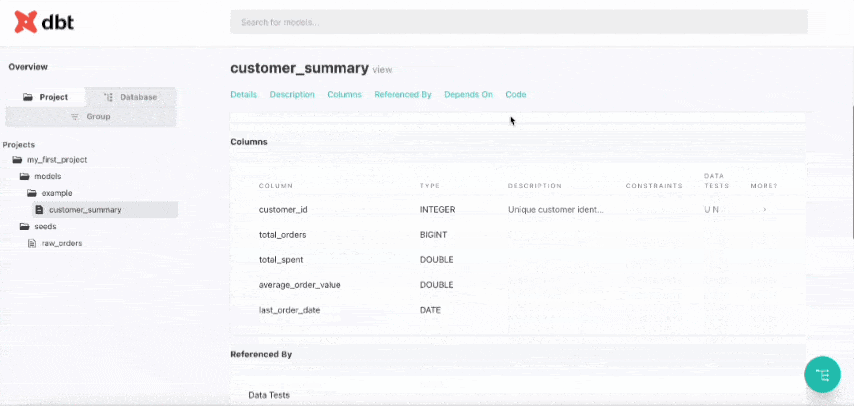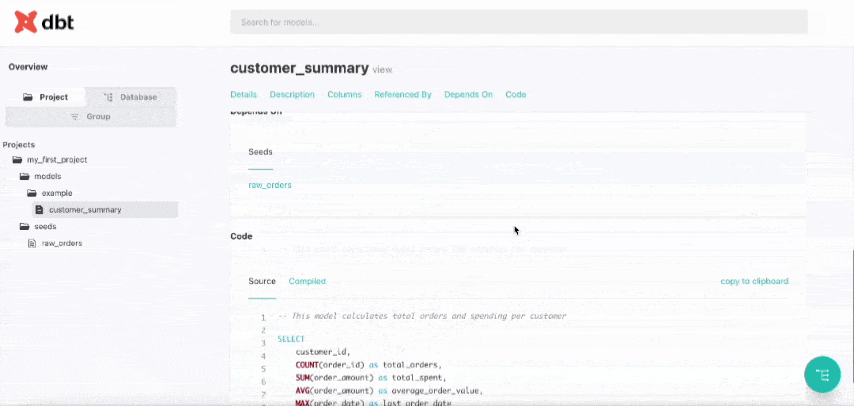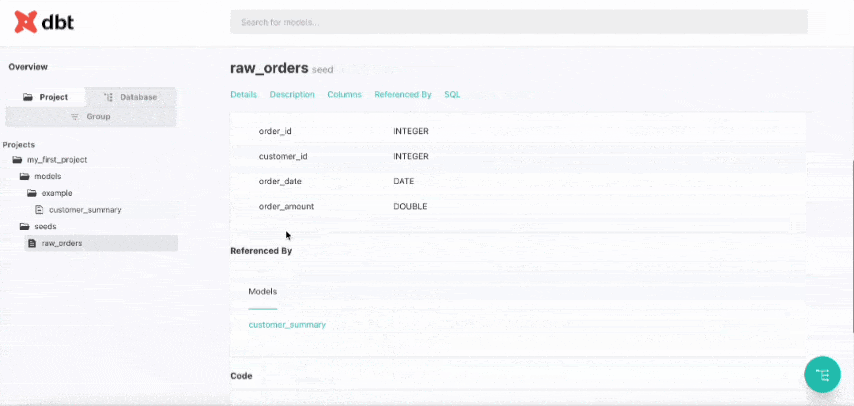
Step 9: Generate Documentation
To create documentation for your models, run:
Your browser will open automatically, displaying a well-designed overview of your entire project.
Press Ctrl + C in Terminal to stop the documentation server.
What Are the Common Use Cases of dbt?
dbt is used across data teams to make transformation work more organized, reliable, and easy to maintain. It’s most often used by teams in these ways:
- Build Clean, Reusable Data Models
dbt helps teams turn unstructured data into models that can be used as the basis for analytics. Analysts make modular changes to SQL queries that the whole company can use. This method reduces errors and ensures everyone uses trusted datasets.
- Creating a Metrics Layer
dbt allows teams to define how business metrics are calculated once, in one place. For example, instead of having five analysts write five different SQL queries to calculate “monthly revenue,” the calculation lives in a single dbt model. The finance team, sales team, and leaders all see the same revenue number because they all use the same model. This gets rid of all the misunderstanding and arguments about whose numbers are right.
- Maintaining Data Quality
Groups can find data issues in dbt before they appear on dashboards. You can check for null values, unique identifiers, proper links between tables, and business logic. These tests protect your data pipeline by running automatically with every transformation.
- Enabling Analytics Engineering
dbt bridges the gap between data engineering and business intelligence. It enables analytics engineers to perform data transformation using software engineering practices such as version control, documentation, and testing.
Best Practices for Using dbt
As you build your dbt project, these practices will help keep it clean and easy to manage.
- Organize Models into Layers
Structure your models folder into clear stages:
- staging: Clean and standardize raw data (one model per source table)
- intermediate: Business logic and joins that aren’t final outputs
- marts: Final models ready for analytics and reporting
This layered approach makes it easier to find models and understand data flow.\
- Document As You Go
Add descriptions to models and columns in your schema.yml files. This will help you and your team in the future. Good documentation explains why a model exists and what decisions were made.
- Write Tests for Everything Important
Don’t skip testing. At a minimum, add tests for:
- Primary keys (unique, not_null)
- Foreign key relationships
- Key business logic
Run dbt test before pushing changes.
- Version Control Everything
Commit your dbt project from the beginning. Use branches for new features, and review changes before merging. This protects your team from mistakenly breaking changes.
- Use Incremental Models for Large Tables
Tables with millions of rows take forever to rebuild. Use incremental models to process only the new or changed data. This saves time and cuts warehouse costs.
How Middleware Enhances dbt Workflows
As dbt projects scale, visibility into performance and failures becomes critical.
Middleware helps data teams monitor dbt performance, detect slow models, and respond to failures before business users are impacted.
Middleware provides comprehensive observability for dbt by monitoring your data pipelines, tracing model execution, and alerting you to performance issues.
What Middleware Provides for dbt Users:
- Data Pipeline Monitoring for dbt
Middleware tracks every dbt run in one place. You can see which models executed, their run times, and success rates. Look at trends over time to spot issues early.
- Tracing for dbt
Middleware traces every dbt model from start to finish. It captures dependencies, execution order, and resource usage. When a model fails or slows down, traces show you exactly where the problem is and which models upstream are affecting it.
- Alerts on Performance Metrics
Set up automated alerts based on dbt performance thresholds. Get notified immediately when:
- A dbt run fails or times out
- Model execution time exceeds your defined limits
- Data quality tests fail
- Resource consumption spikes unexpectedly
This proactive monitoring helps you catch and fix issues before stakeholders are affected.
Setting Up Middleware with dbt
Here’s how to enable monitoring, tracing, and alerts for your dbt project:
- Step 1: Install the Middleware Agent
Since dbt runs on Python, you’ll install the Python agent in your project.
Log in to your Middleware dashboard and navigate to Installation → APM → Python. There, you’ll see the installation guide.
In your project terminal, install the agent:
For profiling support (enables detailed tracing):
- Step 2: Configure Environment Variables
Set up your Middleware credentials and enable profiling for trace collection:
export MW_APM_COLLECT_PROFILING=True
export MW_API_KEY='<your_middleware_api_key>'
export MW_TARGET='https://ccang.middleware.io:443'
export MW_SERVICE_NAME='dbt-example'- Step 3: Run dbt with Monitoring Enabled
Instead of running dbt run directly, use the Middleware wrapper to enable pipeline monitoring and tracing:
middleware-run dbt runThis command runs your dbt transformation while sending performance data, logs, and traces to Middleware.
🚀 Don’t wait for issues to show up in dashboards, catch them early. Middleware helps detect deployment problems, resource spikes, and root causes before they impact users.
Step 4: View Pipeline Metrics and Traces
Go to your Middleware dashboard. You should see your service (e.g., dbt-example) listed under APM services.
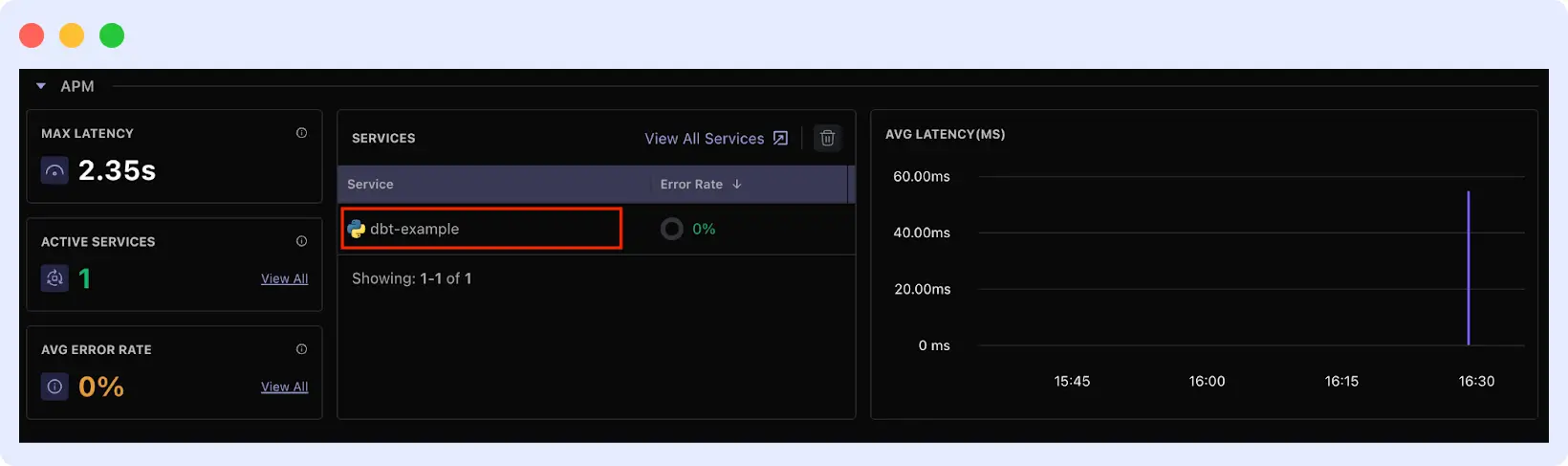
Click on the service to access:
- Success/failure rates of transformations
- Resource consumption during runs
- Query performance breakdown
- Detailed error stack traces when failures occur
- Historical performance trends
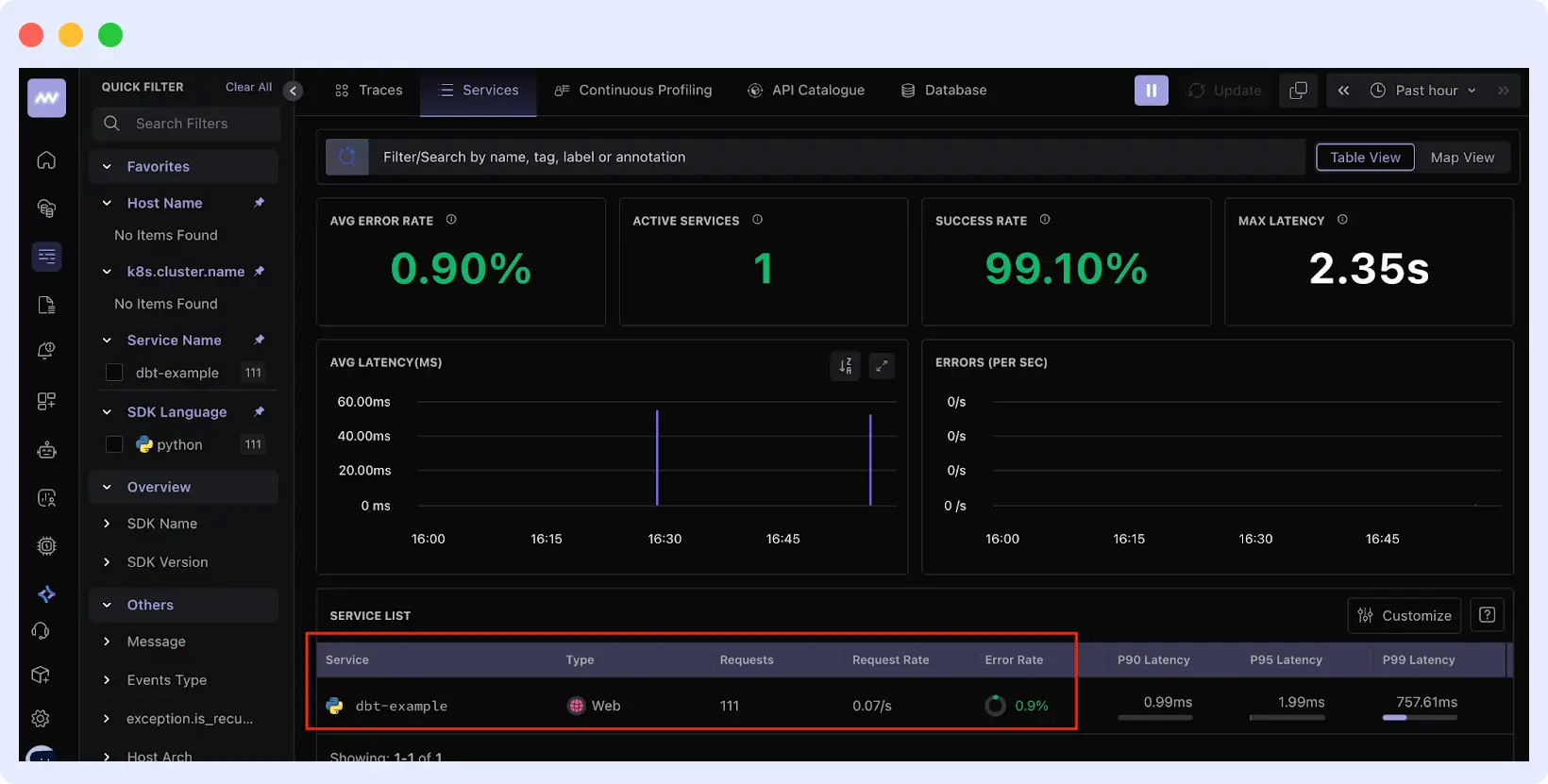
Learn more in the Middleware documentation.
Ready to start?
📌 Want end-to-end observability for your data stack? From data warehouse performance to application reliability, Middleware gives you unified visibility and alerts.🔗 Start a free trial
To set up dbt, follow this guide. Then, use Middleware to keep an eye on your workflows as they grow.
This guide explains how modern data teams use data build tools like dbt to build reliable analytics pipelines. As your data stack grows, combining dbt with observability platforms ensures long-term scalability and trust in data.
FAQ
Is dbt free?
Yes. dbt Core is free and open-source. Install it locally and use it with any data warehouse.
Do I need programming to know programming?
No. You can use dbt if you know SQL. No Python or other languages needed.
Which data warehouse can I use with dbt?
You can use Snowflake, BigQuery, Redshift, Databricks, PostgreSQL, and more.
What’s the difference between dbt Core and dbt Cloud?
Core runs locally via command line and is free. Cloud is browser-based with added features like scheduling, a built-in editor, and team collaboration.
Is dbt suitable for beginners?
Yes. dbt is SQL-based and designed for analysts and analytics engineers. If you know SQL, you can start using dbt without learning new programming languages.