Audit logging is the process of recording every significant event that occurs across your applications, services, and infrastructure, capturing who did what, when, and where.
Audit logs play an integral role in today’s specialized software development landscapes, from cloud-native applications to microservices architectures and containerized environments like Kubernetes.
Whether it’s tracking user access in multi-tenant SaaS platforms, logging configuration changes in DevOps pipelines, or monitoring database transactions in distributed systems, audit logs offer critical insights into system operations. These logs help organizations ensure compliance, diagnose issues in real time, and maintain system integrity across diverse infrastructures like CI/CD workflows, API management, and hybrid cloud platforms.
In this guide, you’ll learn how audit logs work, what they track, and how Middleware simplifies secure, centralized audit logging for compliance and observability.
📘Relevant Read: what is log monitoring?
What is Audit Logging
An audit log tracks a sequence of activities within a system. These log events monitor everything from user actions, such as account creation, to system-level events, such as server configuration changes.
The key components include:
- Event Name: The event that took place, such as “User Logged In” or “File Removed.”
- Event Description: A human-readable summary of the event.
- Timestamp: The time the event occurred.
- Actor: The user or service responsible (e.g., API key or user ID).
- Affected Resource: The app, system, or service where the event occurred.
- Origin Source: Host name, IP, or region in which the action came from.
- Custom Attributes: Middleware lets you tag logs with attributes such as service name, environment, or severity log level for easier filtering.
Middleware enables centralized, immutable log storage with flexible retention policies. You can set how long to keep audit logs based on your compliance needs.
This helps you store logs for as long as needed without incurring high hosting costs. Middleware also encrypts logs and adds tamper protection to maintain audit integrity and safeguard sensitive data.
What is an Audit Trail?
A collection of audit logs forms an audit trail, a sequential record that helps teams track changes across systems over time. Middleware enables you to automatically correlate these trails, allowing you to trace every user action or configuration change across your infrastructure from a single dashboard.
Audit logs vs. Regular logs
While both audit logs and regular system logs capture system activity, they serve different purposes. Audit logs emphasize accountability and help detect potential security incidents by recording actions such as changes to access controls or unauthorized system access.
On the other hand, teams use regular system logs to diagnose errors and troubleshoot issues. For instance, a system log may note a server outage, while an audit log would capture malicious activity like an unauthorized remote shutdown or intentional data deletion.
With Middleware, you can view both audit and system logs in one dashboard, making it easy to distinguish compliance-focused events from operational errors.
The Role of Audit Logs in Development
Now, let’s explore how audit logs contribute to maintaining transparency and control throughout the software development process. You’ll learn how these logs can help ensure accountability, improve debugging and support compliance in your development workflows.
Ensuring Code Integrity
Audit logs monitor every change made during the development lifecycle. For example, if someone pushes unauthorized code to production, the audit log identifies who did it and speeds up resolution.
Debugging and Troubleshooting
Audit logs provide a sequential trail of events, also known as an audit trail, which helps track system changes. Acting like breadcrumbs, they allow teams to follow the exact steps leading to an issue. This detailed audit log is key to diagnosing problems in development, especially when dealing with vulnerabilities posed by threats such as improper access permissions or sensitive data exposure.
In a security breach, audit trails show who accessed sensitive data and when, helping teams fix weak permissions and improve defenses.
Compliance and Security
Audit logs are key to ensuring that development processes meet regulatory compliance requirements, such as GDPR or HIPAA. They track changes to user accounts or sensitive data access, ensuring organizations adhere to strict security controls and privacy regulations.
What Do Audit Logs Track?
Audit logs capture critical activities within systems, providing insights into which actions occurred and who initiated them. Let’s explore some common scenarios that these logs track, highlighting their importance in maintaining security controls:
- Administrative activity: Creating or deleting user accounts or changing access permissions. For example, if a user is removed from a CRM platform like Salesforce, an audit log entry will record this action, detailing the user who made the change and when it happened.
- Data access and modification: Audit logs monitor who accessed or modified sensitive information. For instance, viewing or altering payroll details in a platform like Workday would generate a log entry showing the user, the time of access, and the specific data changed.
- Login failures and user denials: Failed login attempts are logged to alert administrators to potential security events, such as unauthorized access attempts.
- System-wide changes: Infrastructure changes, such as creating virtual machines (VMs) or deploying new services on cloud platforms like Google Cloud, are recorded in audit logs. This helps teams maintain oversight of critical infrastructure adjustments.
For instance, when using Middleware to monitor cloud infrastructure, audit logs can track configuration changes in Kubernetes clusters, API token updates, or unauthorized access attempts within microservices.
How Audit Logging Works?
Middleware collects audit data using lightweight agents and integrations across your services, APIs, and infrastructure.
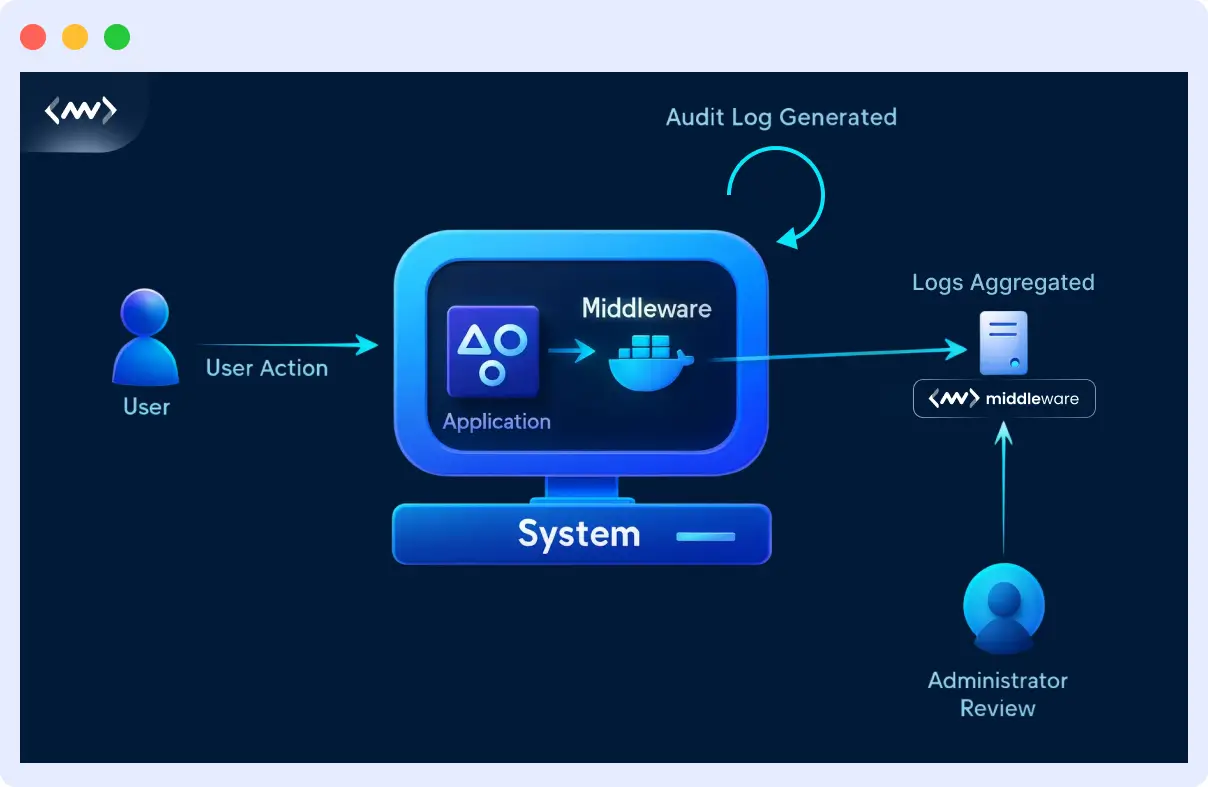
Audit logs depend on centralized log management systems to efficiently gather, store, and analyze data. The process typically involves:
- Log aggregation: Logs are collected from various sources, including applications, databases, cloud platforms, and operating systems.
- Data collection: Each log stores critical details, such as event timestamps, actors (users or systems), and affected resources, making it easier for security teams to track potential threats.
- Analysis in real-time: Once collected, logs are analyzed to detect anomalies, investigate incidents, and generate compliance reports.
For instance, AWS CloudTrail aggregates logs from resources such as EC2 instances and S3 buckets, giving teams visibility into system activities and resource changes.
Once collected, Middleware analyzes logs in real time to detect anomalies, generate compliance-ready reports, and provide unified visibility across environments.
Benefits of Audit Logging
Audit logs serve as a vital tool for maintaining the integrity, security, and reliability of your systems. By providing a record of events, they help organizations meet regulatory compliance, troubleshoot issues, and protect against threats. Below are some key benefits of effective audit logging:
- Ensuring compliance: Audit logs provide proof that systems adhere to regulatory standards, such as PCI DSS or SOC 2, set by industry authorities, or to internal controls. They ensure that your system meets the required benchmarks for handling sensitive data and security.
- Incident reconstruction: When a security incident or outage occurs, audit logs help trace the sequence of events leading up to it. For example, after a breach, logs identify who accessed the system, when they did it, and the actions they performed.
- Operational troubleshooting: Audit logs help teams find the root cause of system failures and improve transparency. For example, if a payment gateway goes down, logs show whether it was an internal error or a manual action.
- Providing verifiable evidence: Audit logs give accurate evidence for internal reviews, supporting transparency and efficient operations. For example, logs can show who authorized a transaction or update, ensuring transparency in critical environments.
- Real-time threat detection: Middleware monitors audit logs for anomalies and risks, helping you respond quickly before issues escalate.
Stop firefighting, start preventing. 🔎
Resolve root causes before users feel the impact.
Real-world Use Cases for Audit Logs
Now, let’s explore some real-world applications where audit logs play an essential role in helping companies across various industries:
- In security monitoring, audit logs provide real-time insights into system activity. By logging each login and resource access, they help detect unusual activity and quickly prevent unauthorized access.
- In regulated industries like healthcare and finance, these logs are vital for compliance with laws such as GDPR and HIPAA. Every access to sensitive data is logged, giving businesses clear records for audits and compliance checks.
- For operational troubleshooting in cloud-based infrastructures, audit logs capture downtime, service modifications, and misconfigurations across distributed systems. This visibility helps engineers quickly identify performance issues and maintain system stability.
- In DevOps and continuous delivery pipelines, these logs help track code deployments and system changes. By recording each change, teams can trace failures quickly and maintain code integrity during development.
By adopting audit logs, businesses can strengthen system oversight, boost security, and streamline regulatory compliance.
What are the Challenges in Audit Logging
Managing audit logs effectively can be challenging in modern distributed systems. From deciding what to log to keeping logs tamper-proof and scalable, teams often face trade-offs between visibility, cost, and security.
Balancing Log Volume
Collecting too many logs can strain storage and processing resources, but logging too little leaves gaps in event tracking. For example, logging every API call could generate excessive data, while missing failed login attempts may overlook potential security threats.
Preventing Unauthorized Access and Data Exposure
Sensitive details, like access keys or passwords, should be carefully excluded from logs. For instance, logging plain-text credentials exposes security risks if an attacker gains unauthorized access to these logs.
Ensuring Log Correlation in Distributed Environments
In distributed systems, connecting logs from different services can be difficult. Middleware simplifies this by automatically correlating logs from multiple environments, enabling teams to trace a single event, such as a user permission change, across the entire system in real time.
Retention and Storage Costs
With organizations generating terabytes of log data daily, long-term storage can become costly. Middleware optimizes retention by allowing teams to define storage policies that archive critical audit trails while keeping recent data instantly searchable.
What are the Best Practices for Audit Log Management
Effectively managing audit logs is essential for tracking system activity, meeting compliance, and addressing potential risks. Below are five best practices to help manage logs efficiently and address key challenges such as data integrity & access control.
Set Retention Policies
Establish a precise retention period for audit logs in line with regulatory guidelines and organizational needs. For example, GDPR mandates keeping logs for 5 to 7 years.
Setting appropriate retention periods ensures logs are available for future audits while preventing excess data accumulation, which can lead to storage overload and higher costs. This practice also helps avoid the risk of deleting essential logs too early or keeping irrelevant data for too long.
Ensure Immutability
Store logs in a tamper-proof format, such as encrypted or blockchain-based records, to prevent unauthorized changes. Logs should remain unaltered from the moment they are created to maintain integrity. If logs are tampered with, their credibility is lost, undermining your ability to track events accurately, especially during audits or investigations.
Centralized Log Management
Instead of scattering logs across different platforms and systems, use a centralized log management solution. Collecting logs from multiple sources—such as applications, cloud platforms, and servers—into a single location enables quicker searching, correlation, and analysis. This centralization also simplifies monitoring and reporting across complex, distributed systems.
Middleware provides a unified platform for aggregating and analyzing all your logs in one place, ensuring consistency and faster issue detection.
🔍Want full visibility across all your logs?
Explore Middleware Log Explorer and monitor every event in real time.
Regular Monitoring
Consistently monitor audit logs to detect anomalies, unusual access patterns, or suspicious activity before they escalate into serious security breaches. Using observability tools like Middleware, you can monitor these logs in real time and receive alerts to resolve issues before they escalate quickly.
Implement Access Control
Limit who can view or modify audit logs to prevent misuse. You minimize the risk of internal tampering or accidental deletions by restricting access to key personnel, such as administrators. For example, sensitive logs containing user activity or critical system changes should be off-limits to unauthorized users.
Centralize and Analyze Audit Logs with Middleware
Middleware Log Management allows teams to aggregate and search audit logs across all applications, cloud environments and third-party systems using lightweight agents and integrations. Logs are securely stored and support customizable retention policies to facilitate long-term review and compliance.
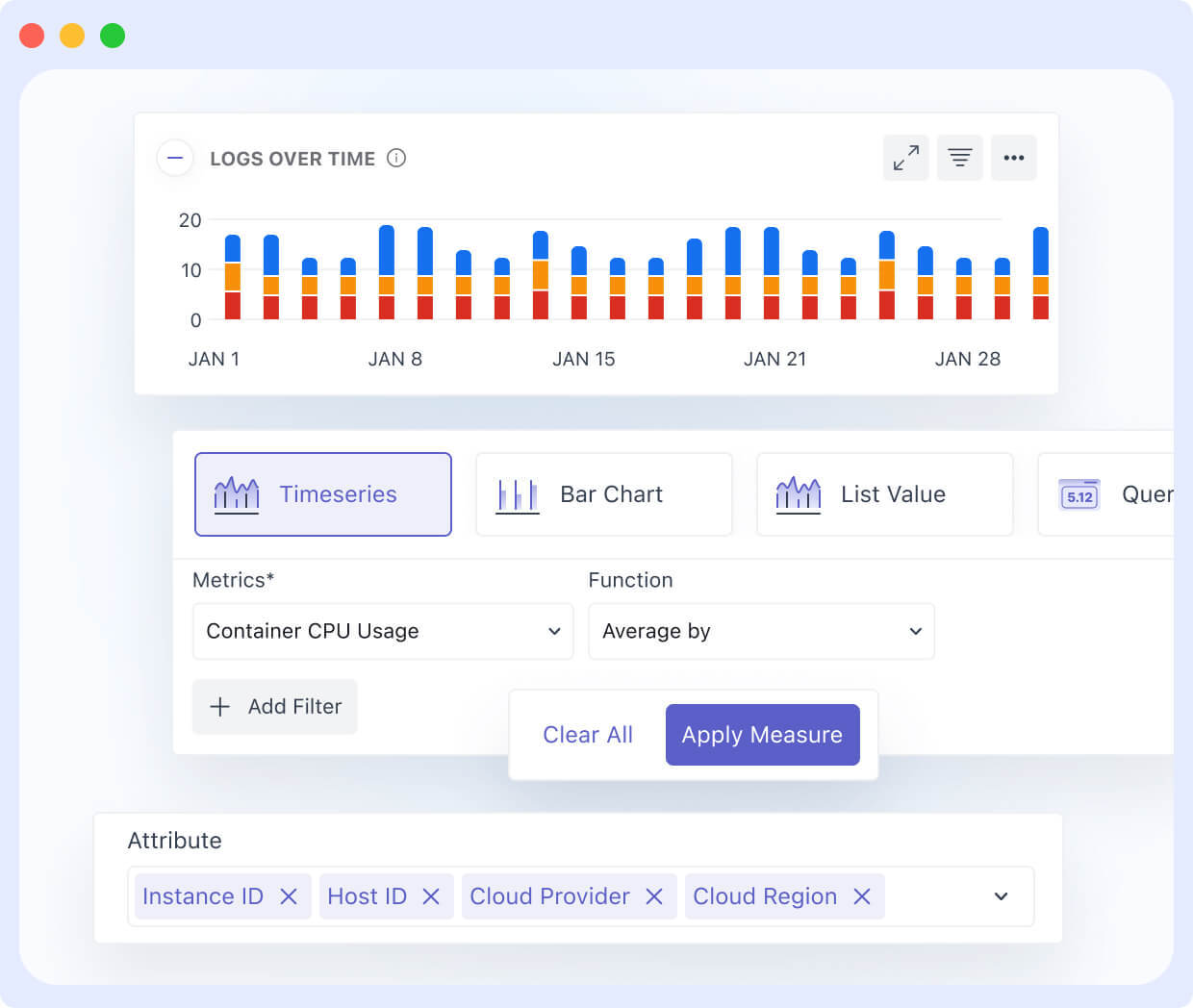
With Middleware’s Audit Log Explorer, you can see every configuration change, API call, and system event in real time, making it easy to audit incidents, monitor activity, and maintain complete visibility of your stack.
Final Thoughts
Audit logs have become essential for managing complex systems. They help track issues and provide deeper insights through real-time monitoring and advanced log audits. New trends like AI-driven anomaly detection help organizations spot threats early. Cloud-native logging solutions also make it easier to manage distributed systems.
With infrastructure expansion, it’s essential to adopt audit logs alongside modern observability tools. This approach ensures compliance is consistently met, debugging becomes more efficient, and system operations remain transparent.
As organizations evolve, these tools give clear insights into system behavior. They help teams resolve issues quickly and maintain control over complex environments. Now is the ideal time to integrate these practices to reinforce your system’s reliability and adaptability.
With Middleware, organizations can centralize audit logs, automate compliance checks, and gain real-time insights into security and performance.
What is an audit log?
An audit log is a detailed record of system activities, capturing events like user actions or system changes. It helps track who did what, when, and where in a system, making it crucial for accountability and troubleshooting.
What should be included in an audit log?
An audit log typically includes the event name, timestamp, the actor (e.g., user or service), and details about the impacted system, offering a clear trail of actions.
What are the two types of audit logs?
Audit logs often fall into two main categories: system logs, which track technical operations, and security logs, which focus on access control and sensitive actions.
What is the difference between audit logs and activity logs?
While audit logs emphasize security and compliance, activity logs track broader user behavior without necessarily meeting strict regulatory requirements.
How does Middleware simplify audit log management?
Middleware automatically collects, correlates, and centralizes audit logs from all your environments, cloud, containers, APIs, and databases, helping teams quickly identify issues and ensure complete visibility across distributed systems.
Why are audit logs necessary for compliance?
Audit logs help demonstrate adherence to compliance frameworks, such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR, by providing a verifiable trail of all system activities. Middleware ensures audit logs are tamper-proof and securely stored, making compliance audits faster and more reliable.
What’s the difference between audit logs and event logs?
Audit logs focus on who did what and when, emphasizing accountability and security. Event logs, on the other hand, capture system performance or operational events (e.g., CPU spikes or app errors). Middleware enables you to view both in a unified dashboard, simplifying analysis.